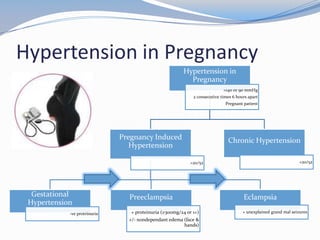
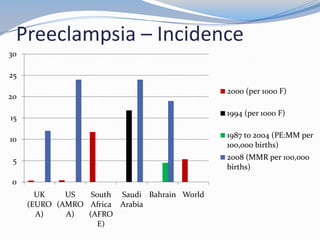
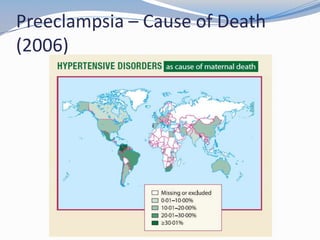
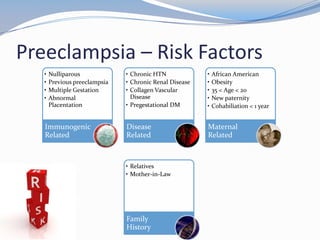
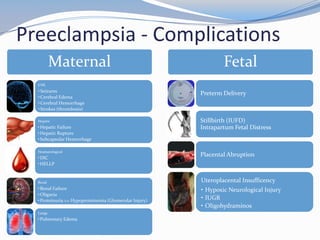
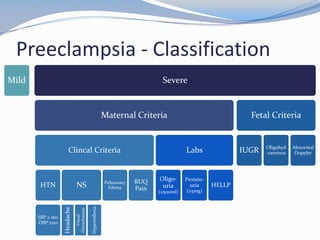
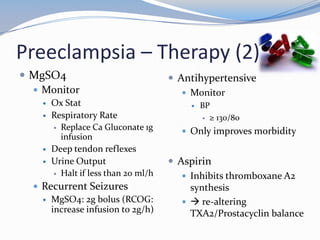
This document discusses hypertension in pregnancy and preeclampsia. It begins by outlining normal blood pressure changes during pregnancy, then defines pregnancy-induced hypertension and chronic hypertension. It distinguishes between gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia. Preeclampsia is defined as new onset hypertension and proteinuria after 20 weeks of gestation. Risk factors, incidence rates, causes, pathophysiology, complications, classification, diagnosis, and management of preeclampsia are then summarized. Indications for delivery are outlined for both mild and severe preeclampsia cases based on maternal and fetal stability and gestational age.