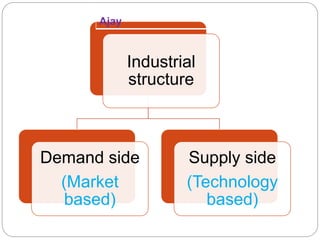
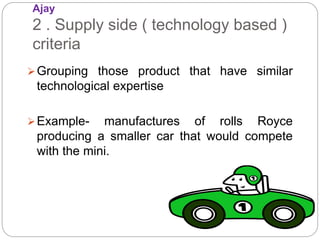
The document discusses different types of industrial and market structures. It defines industrial structure as a group of firms that produce close substitute goods for a common group of buyers. Industrial structure can be analyzed from a demand-side perspective based on how consumers distinguish products, or a supply-side perspective based on similar production technologies.
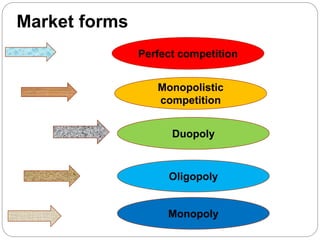
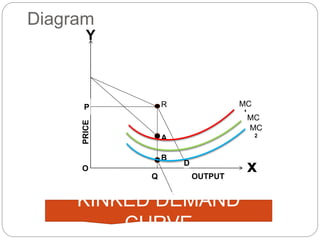
The document then discusses different market structures - perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly. It provides characteristics of each structure such as the number of buyers and sellers, product differentiation, barriers to entry. It also explains key concepts like kinked demand curves in oligopolistic industries where prices tend to remain rigid over long periods.