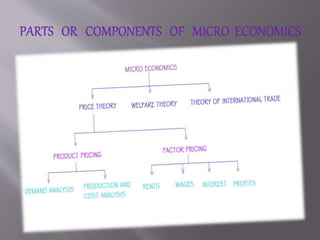
Economics is the study of how people and societies make choices about production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It explains phenomena like rising food costs when gas prices increase and why countries and politicians worry about bankruptcy. Economics looks at how individuals and groups interact in markets to satisfy wants and needs. It is divided into microeconomics, which examines individual agents and markets, and macroeconomics, which looks at aggregates and the overall economy.