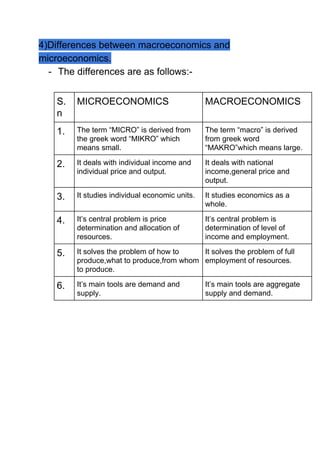
Macroeconomics studies the economy as a whole and focuses on aggregate economic variables such as national income, output, employment and general price levels. It has four main uses: 1) understanding how the economy works; 2) formulating economic policies; 3) making international comparisons; and 4) informing business decisions. The scope of macroeconomics includes theories related to national income, employment, money, prices, and economic growth. It differs from microeconomics in that macroeconomics examines the large-scale or overall economy rather than individual agents.