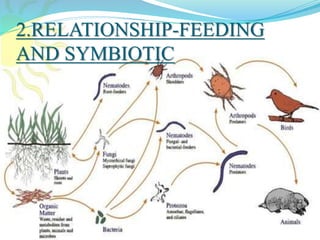
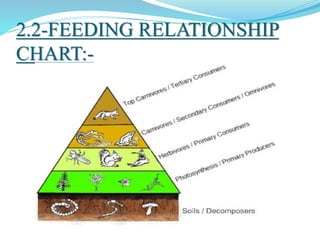
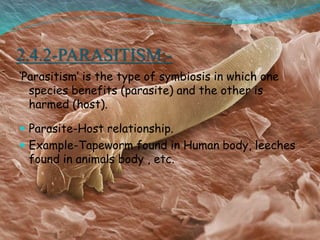
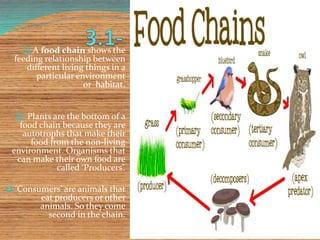
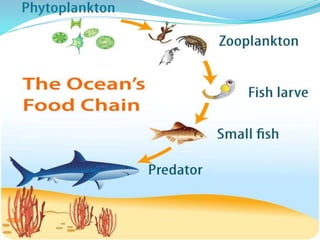
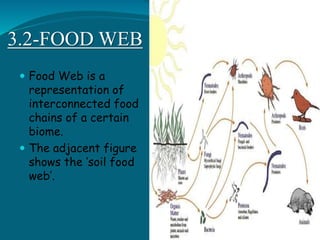
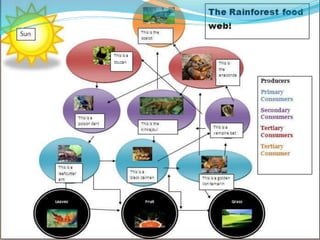
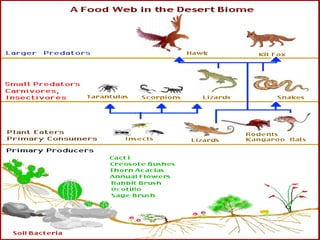
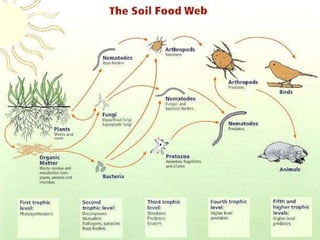
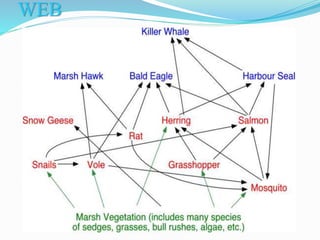
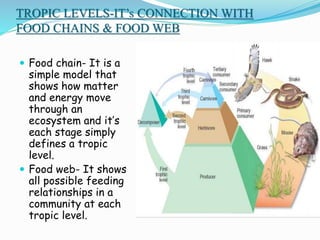
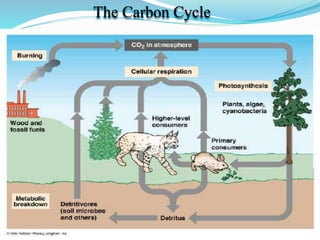
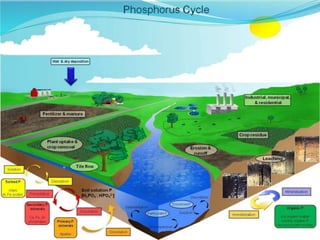
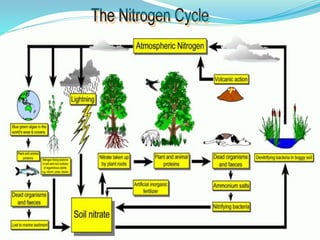
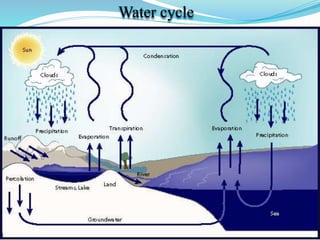
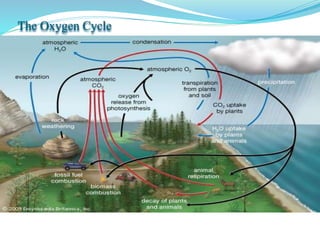
The document provides an extensive overview of ecology, defining key concepts such as organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes, as well as discussing symbiotic relationships among species. It outlines various feeding relationships and the roles of different groups of organisms, including producers, consumers, and decomposers. Additionally, it describes essential biogeochemical cycles including the carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen, water, and oxygen cycles, highlighting their significance in ecosystem functioning.