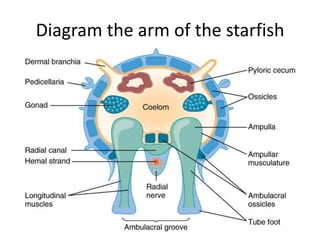
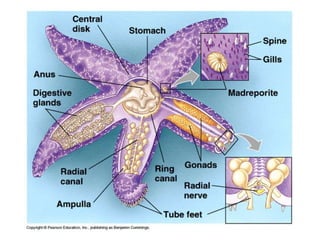
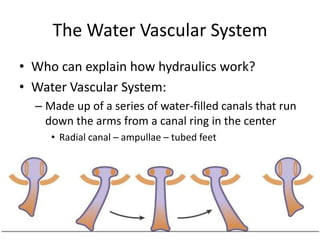
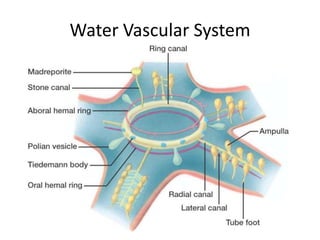
Echinoderms are marine invertebrates with spiny skin and five-part radial symmetry. They have a water-vascular system and tube feet used for movement. There are five classes of echinoderms: sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and sea lilies. Sea stars have tube feet and a water vascular system that allows them to move and catch prey as carnivores. Sea urchins also have tube feet and move by grazing on algae and plants as herbivores. Sea cucumbers use their tube feet to move and take nutrients from sand with oral tentacles.