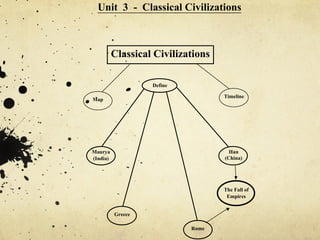
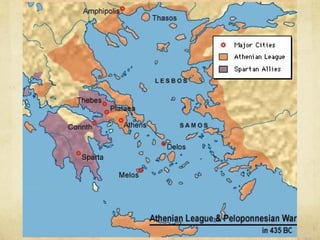
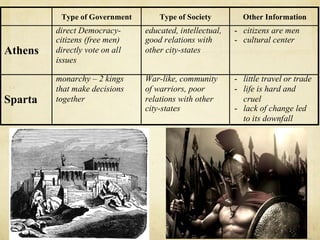
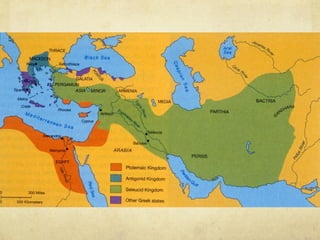
Unit 3 discusses classical civilizations such as Greece, Rome, Maurya India, and Han China. Key events included the rise of city-states in Greece like Athens and Sparta, Alexander the Great's conquests, and the spread of Hellenistic culture. The unit provides a timeline of classical civilizations and examines their governments, societies, and contributions to modern society like classical architecture, philosophy, and democracy.