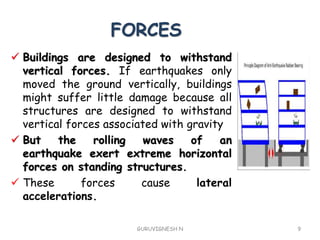
This document discusses resilient structural systems for earthquake resistance. It provides 3 key points:
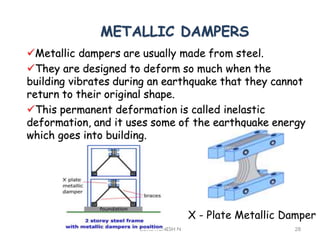
1. Including mechanical devices in structures can enhance performance during extreme loads like earthquakes by providing strength while controlling behavior to protect elements from damage. Systems can be designed to fuse during strong ground motions.
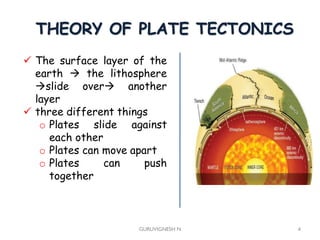
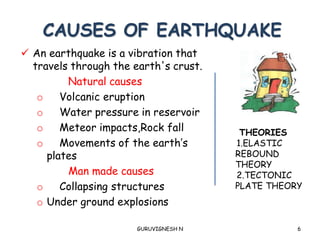
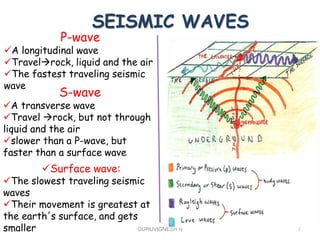
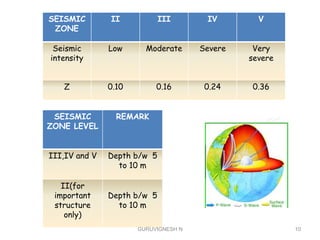
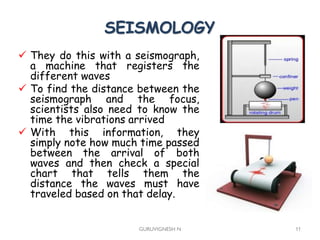
2. Earthquake waves are studied using seismology to understand quake magnitude, location, and predict future events. Structures are designed according to seismic zone levels based on past quake intensities.
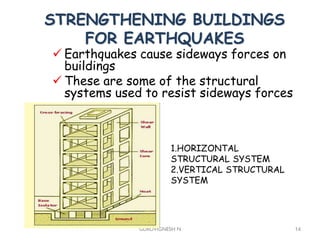
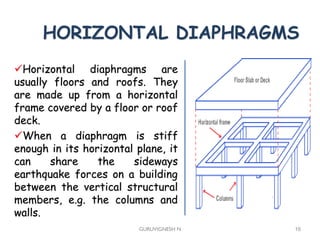
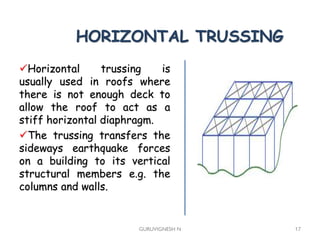
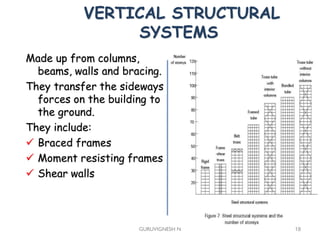
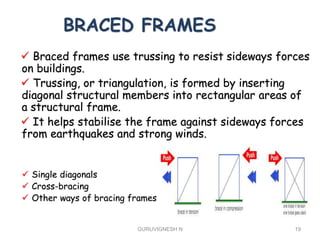
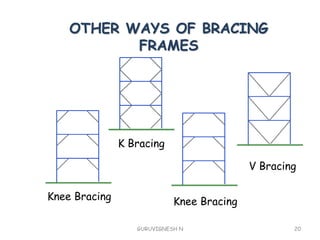
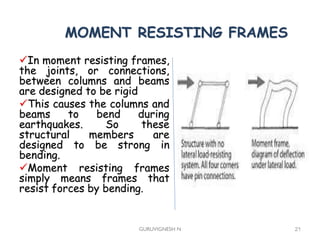
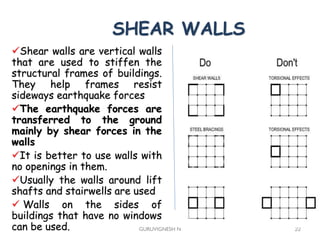
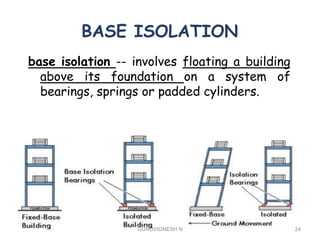
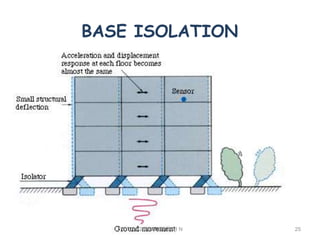
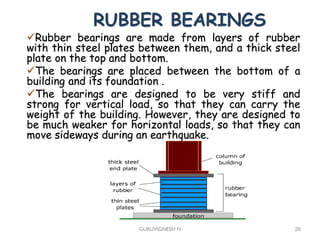
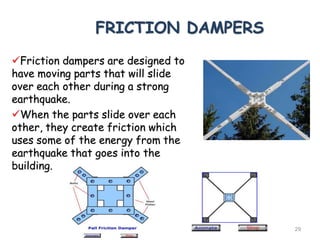
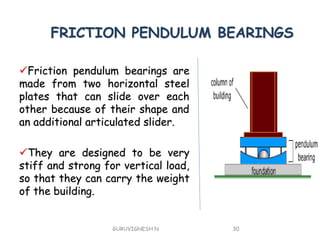
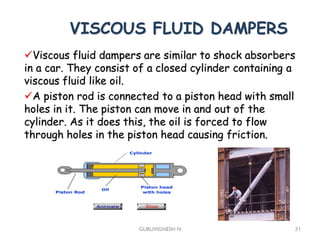
3. Common earthquake-resistant building techniques include base isolation, dampers, braced frames, shear walls, and stiff horizontal diaphragms/trusses to distribute seismic forces across the vertical structure. Tall buildings