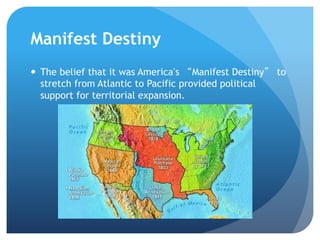
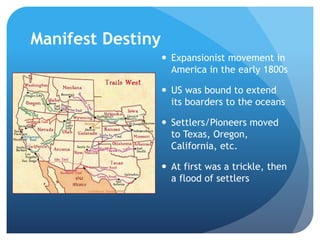
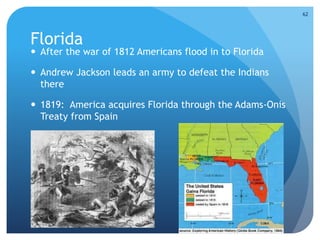
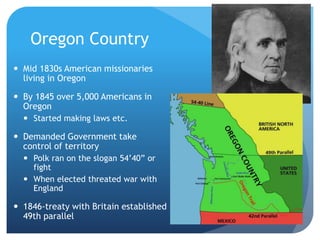
This document provides an overview of the Early National Period in the United States from 1789-1848. It summarizes key events and developments, including:
- George Washington's presidency and establishment of neutrality in foreign affairs.
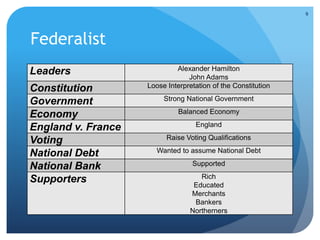
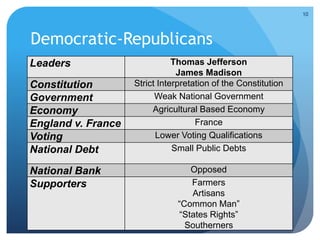
- The emergence of political parties (Federalists and Democratic-Republicans) and early domestic controversies over issues like the National Bank.
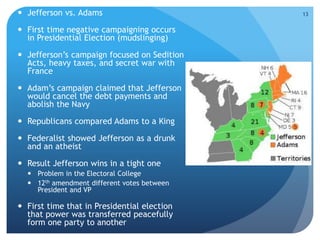
- The presidencies of John Adams and Thomas Jefferson and partisan conflicts over foreign policy with England and France.
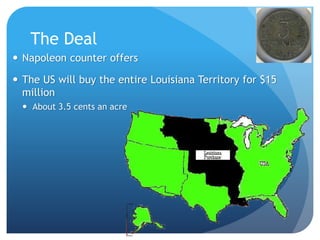
- Westward expansion through the Louisiana Purchase and Lewis and Clark Expedition, as well as growing sectional tensions over the expansion of slavery.
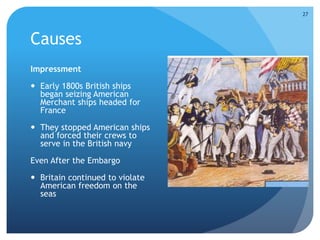
- The War of 1812 and its impact on national identity and manufacturing growth