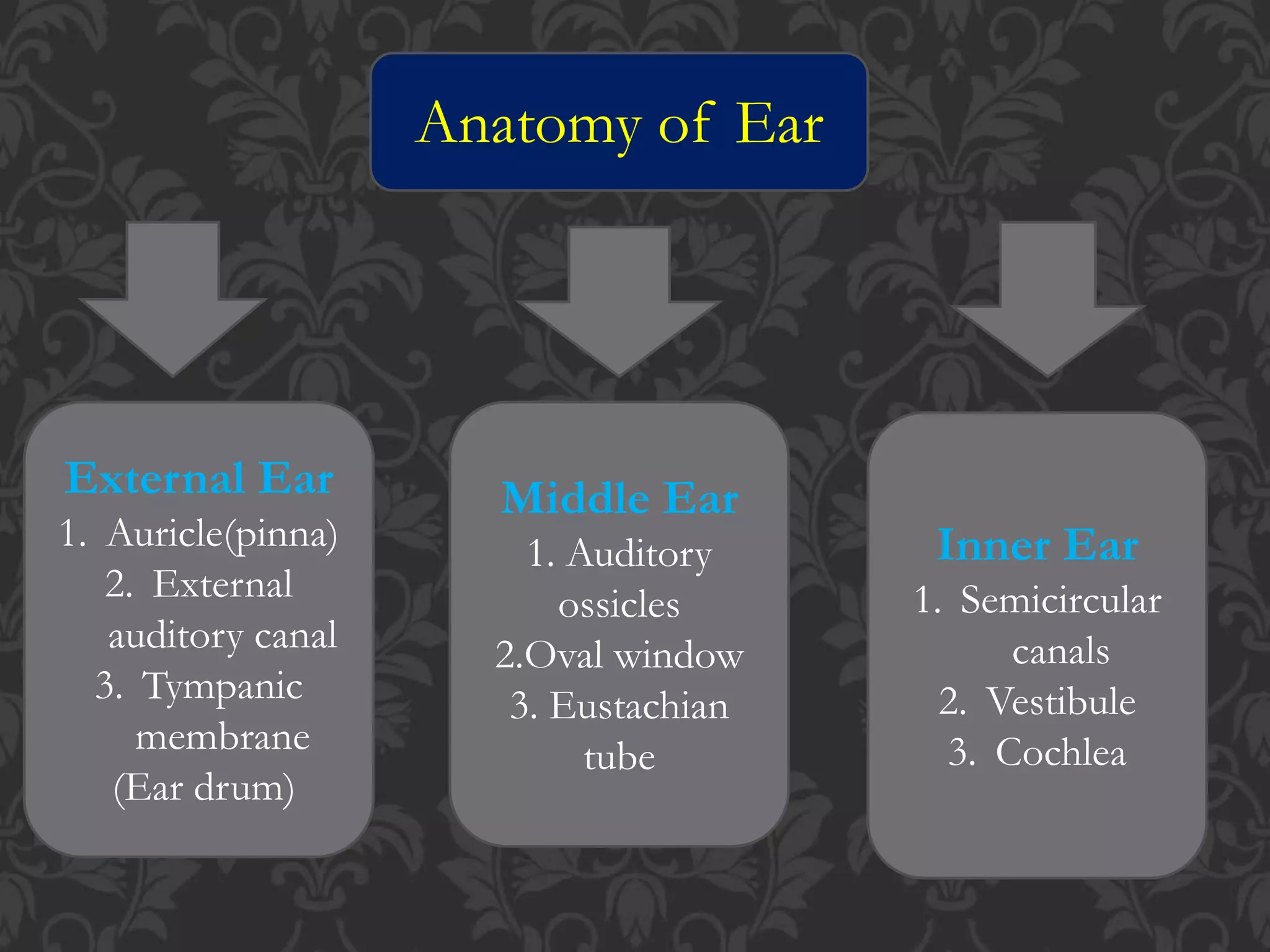
The document summarizes the anatomy and physiology of the human ear. It is divided into three main sections - the external, middle, and inner ear. The external ear includes the pinna, external auditory canal, and eardrum. The middle ear contains the three smallest bones in the body known as the auditory ossicles which transmit sound from the eardrum to the inner ear. The inner ear is made up of the semicircular canals for balance and the cochlea, which converts sound waves into nerve signals for hearing.