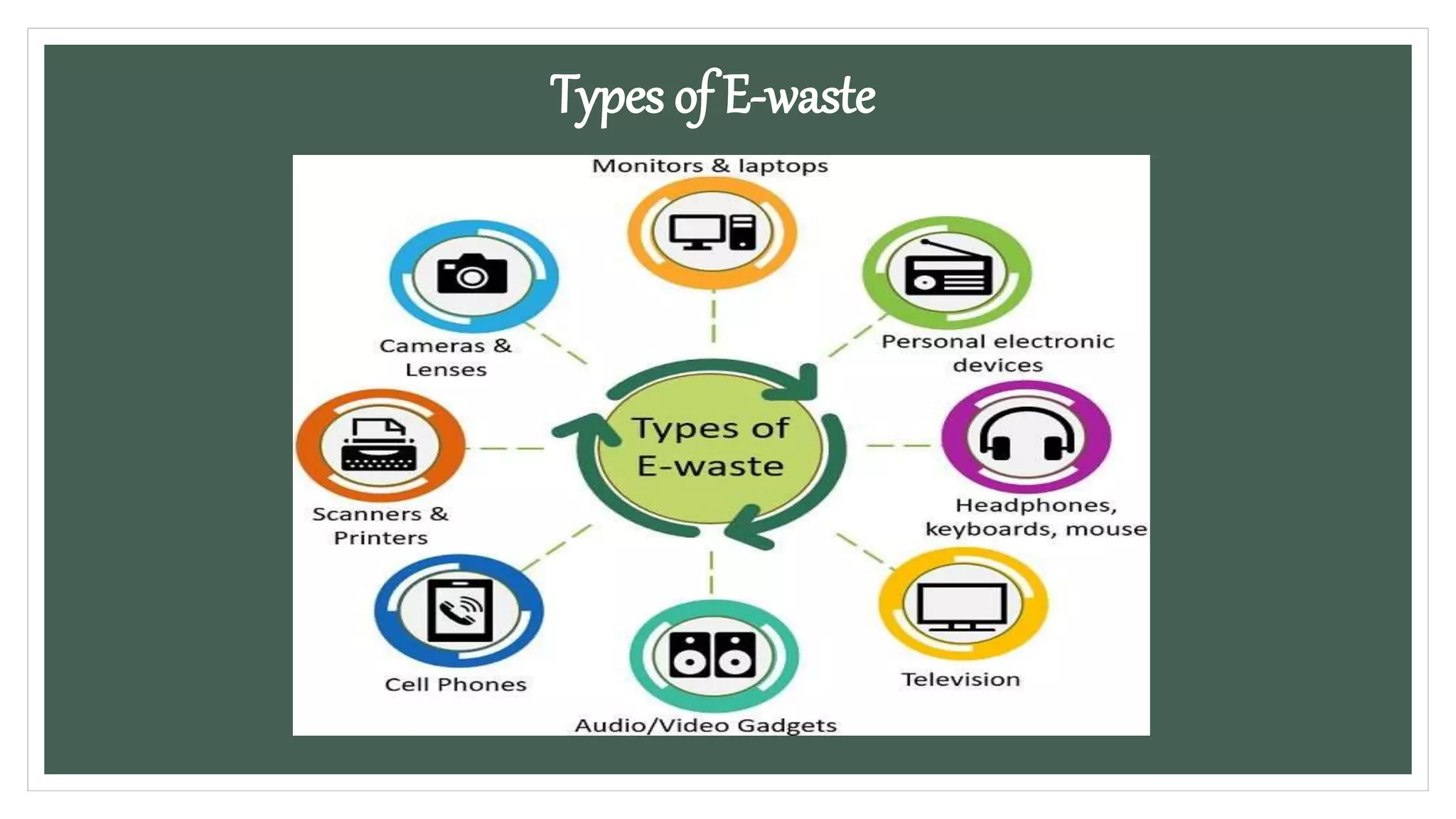
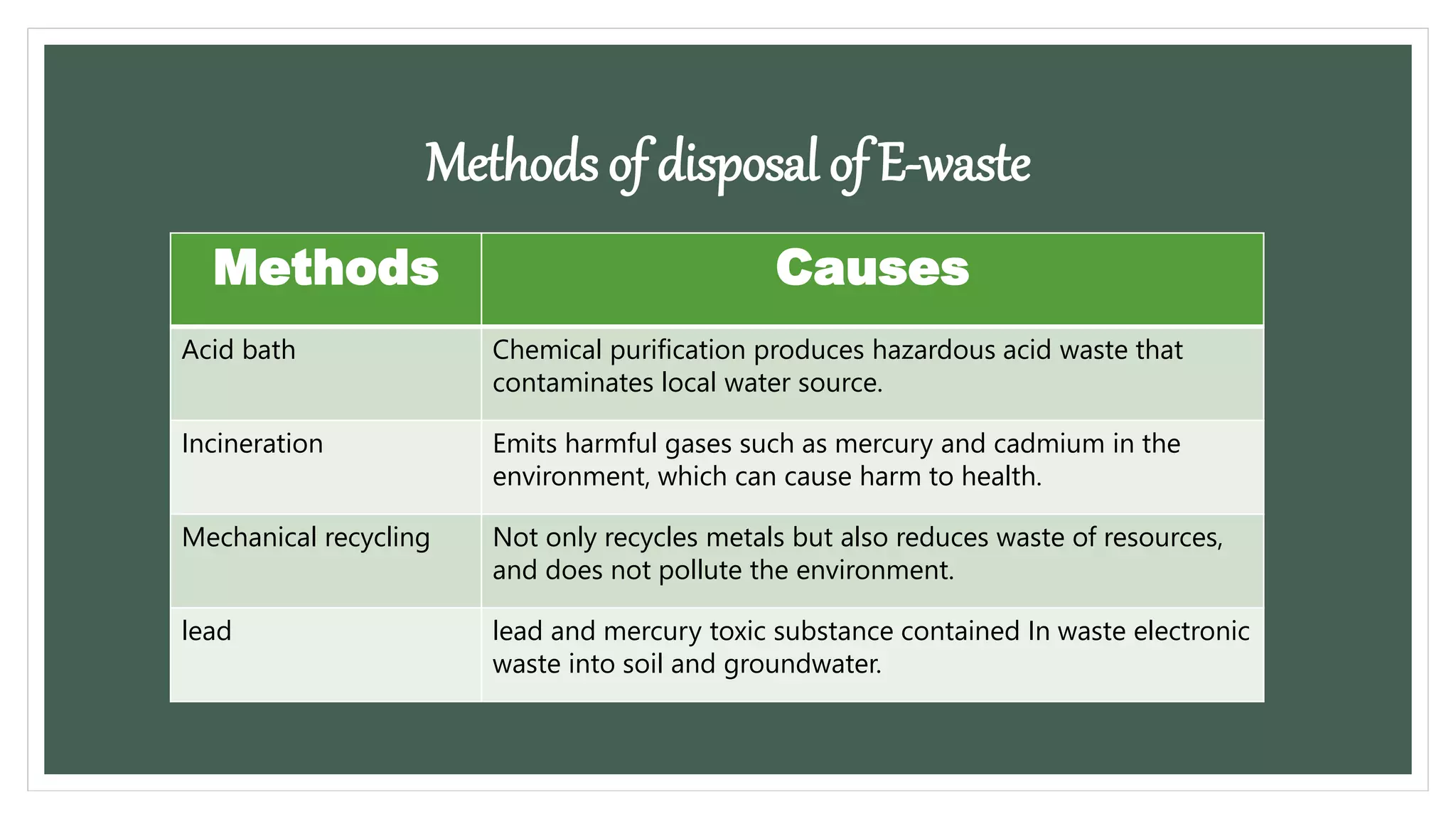
E-waste refers to electronic devices that are no longer useful, such as old phones, computers, and televisions. These devices contain hazardous materials like lead and mercury that can harm the environment and human health if improperly disposed. Common sources of e-waste include large and small household appliances, IT equipment, and audio/visual devices. Improper e-waste disposal methods like acid baths and incineration release toxic fumes, while landfilling allows chemicals to leach into soil and water sources. The volume of e-waste produced annually is growing rapidly and most is improperly disposed of rather than recycled.