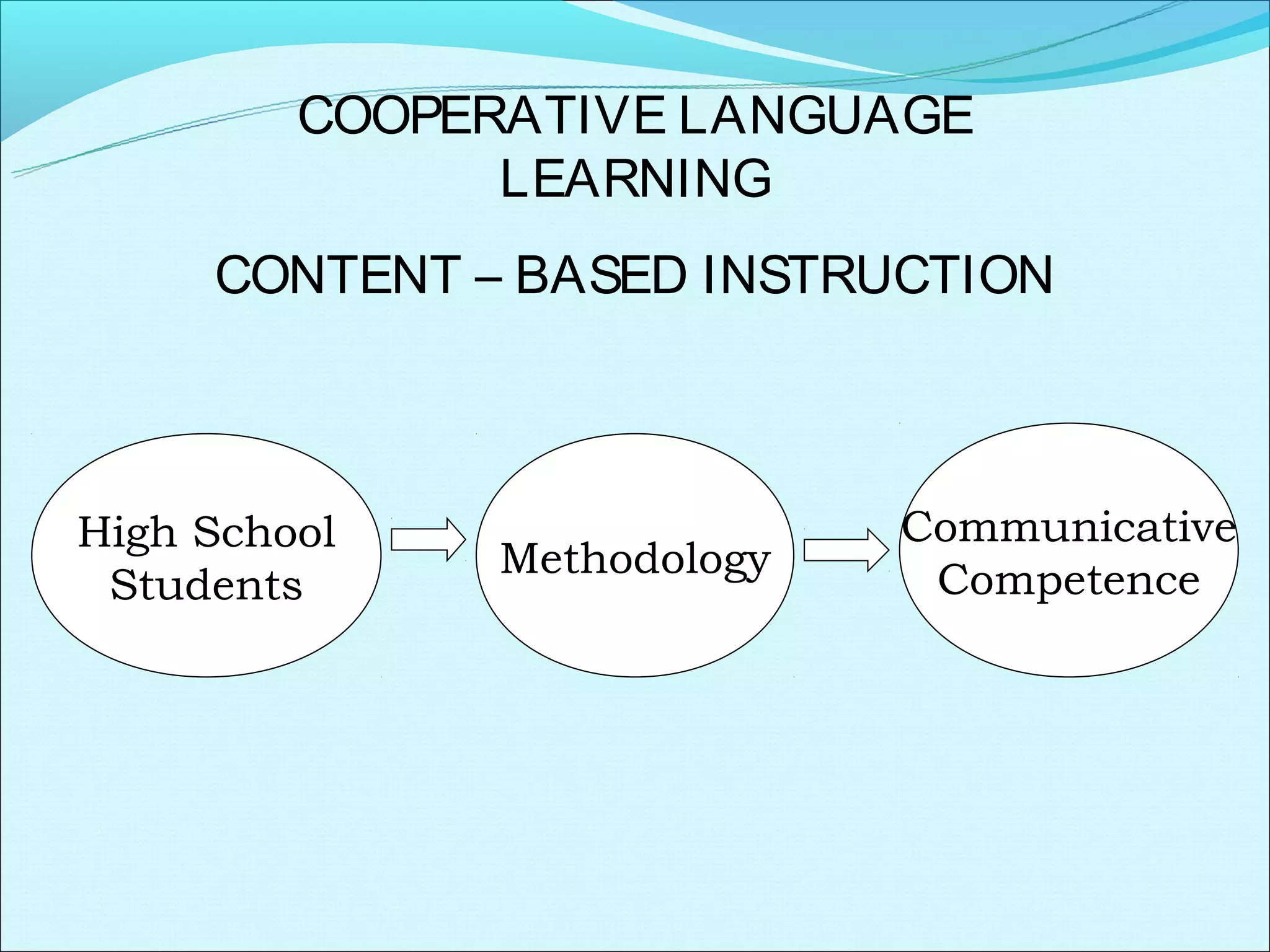
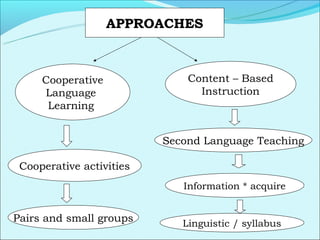
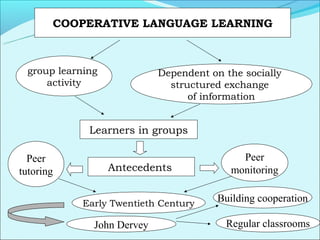
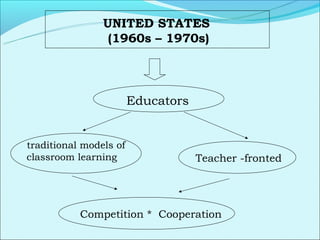
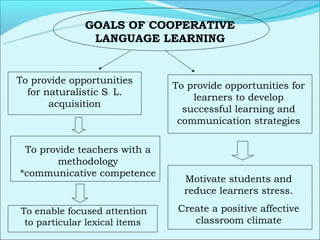
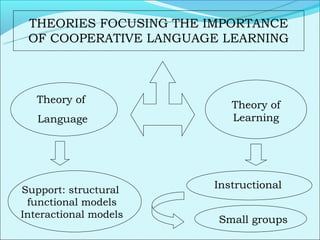
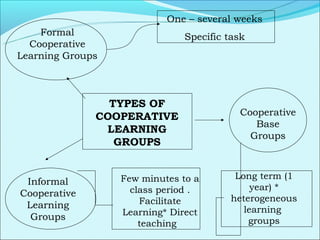
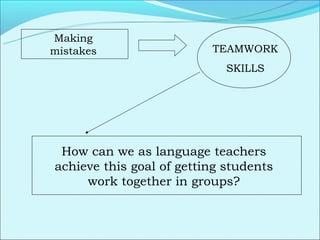
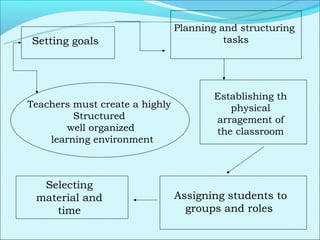
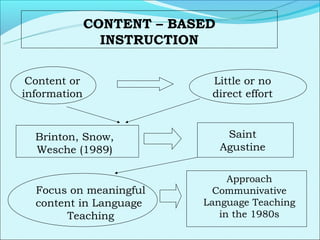
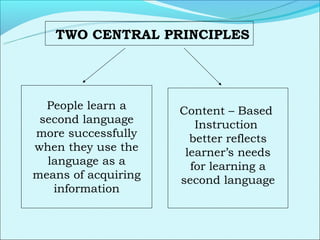
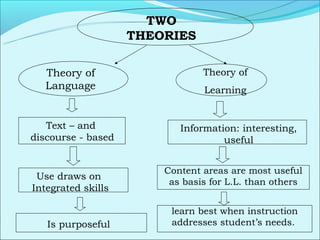
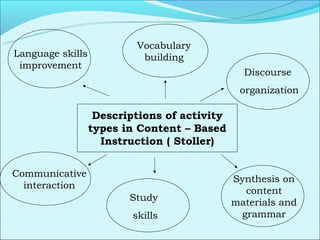
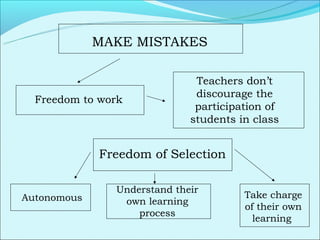
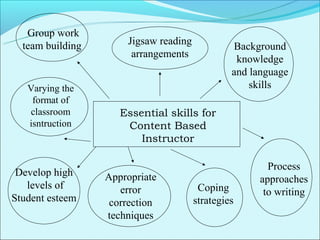
Cooperative language learning (CLL) and content-based instruction (CBI) are approaches to second language teaching that focus on group work and learning content through the target language. CLL uses pair and small group activities to promote natural language acquisition, while CBI integrates language skills and content learning. Both aim to create a communicative environment where students work cooperatively to build language proficiency and content knowledge.