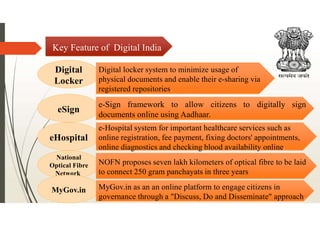
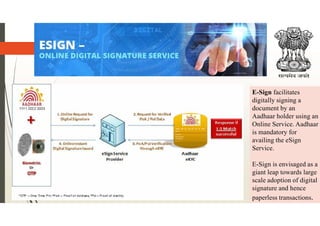
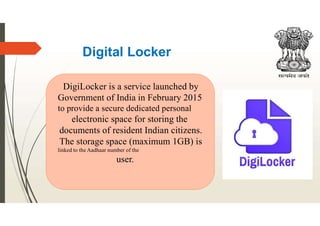
Digital India, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on July 1, 2015, aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society through initiatives focused on digital infrastructure, governance, and citizen empowerment. Key features include programs like e-sign, digital lockers, and e-hospital services, while advantages encompass transparency, improved service quality, and reduced corruption, against challenges such as digital illiteracy and cybersecurity threats. The initiative is underscored by nine pillars, including universal mobile connectivity and e-governance, promoting significant advancements in technology-led service delivery.