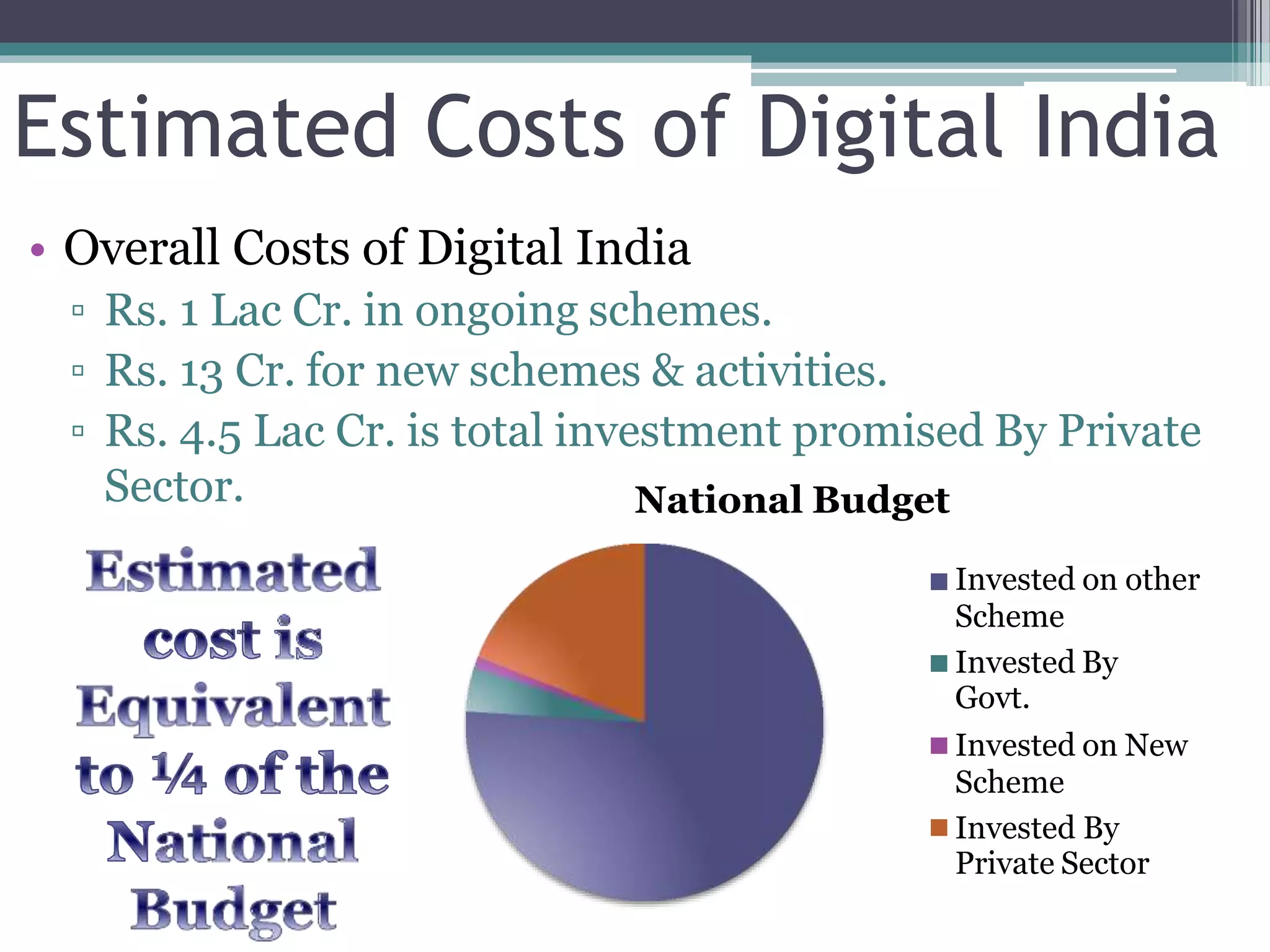
The document outlines India's "Nine Pillars" strategy for its Digital India initiative. It discusses pillars such as expanding broadband connectivity to rural areas, increasing public internet access points, implementing e-governance reforms, and developing skills for jobs in the IT industry. The overall cost of Digital India is estimated at Rs. 1.4 trillion, with Rs. 1 trillion already allocated to ongoing schemes and Rs. 130 billion for new schemes. Private sector investment is expected to reach Rs. 4.5 trillion. Challenges to implementation include high digital illiteracy, connecting remote areas, and ensuring cyber security. If successful, Digital India has the potential for major social, economic, and environmental impacts in India.