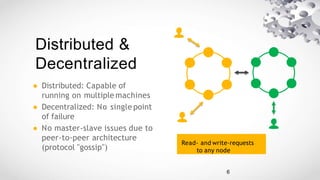
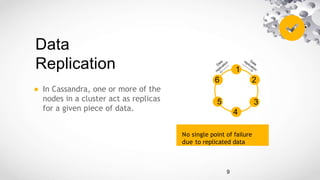
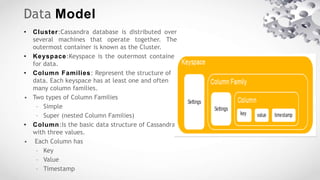
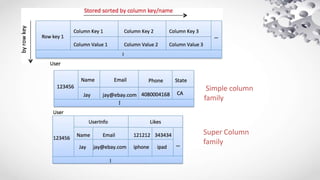
Cassandra is an open source, distributed database management system designed to handle large amounts of data across many commodity servers. It provides high availability with no single point of failure, linear scalability and performance, as well as flexibility in schemas. Cassandra finds use in large companies like Facebook, Netflix and eBay due to its abilities to scale and perform well under heavy loads. However, it may not be suited for applications requiring many joins, transactions or strong consistency guarantees.