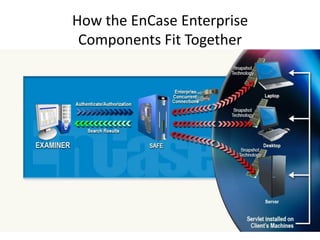
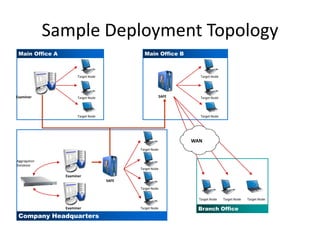
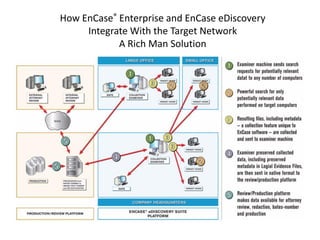
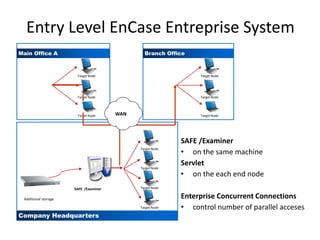
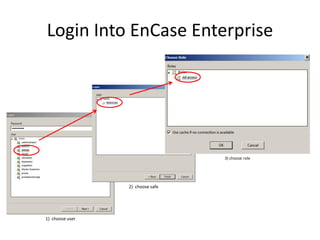
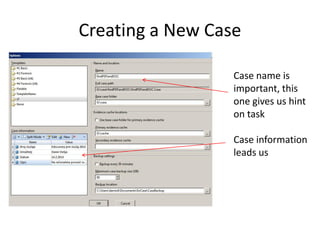
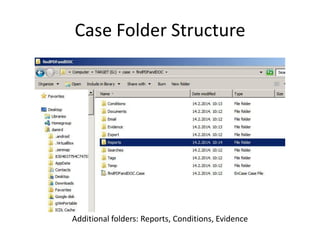
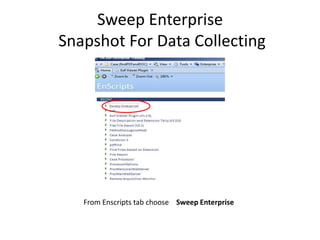
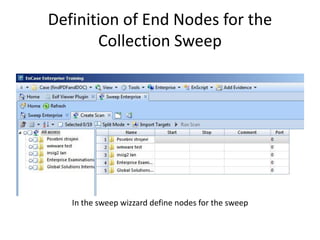
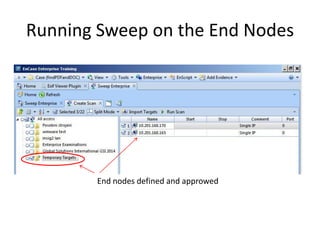
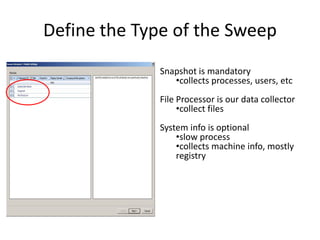
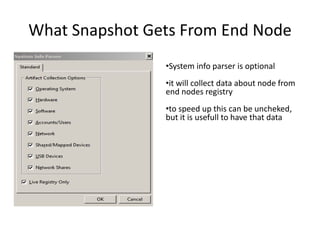
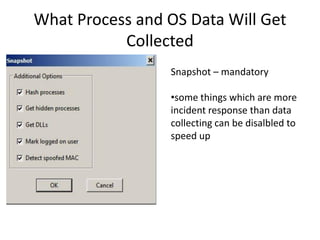
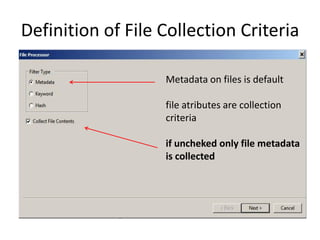
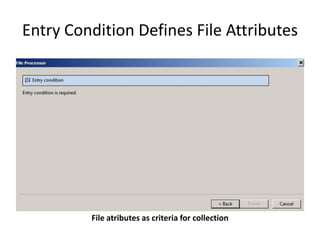
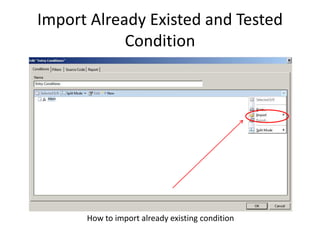
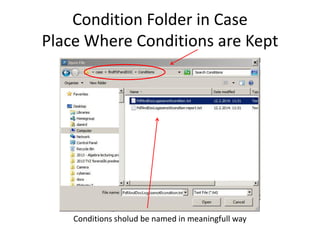
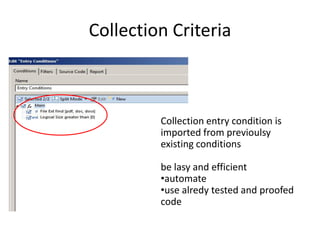
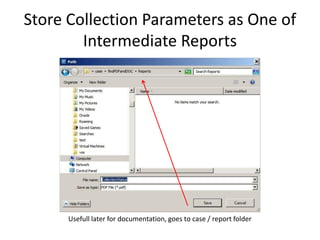
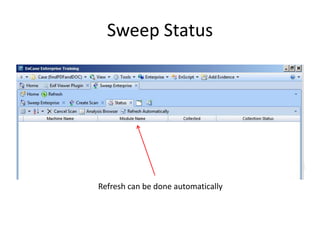
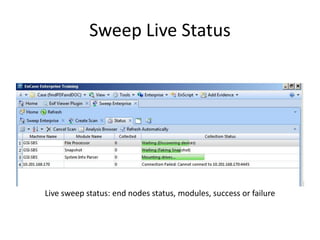
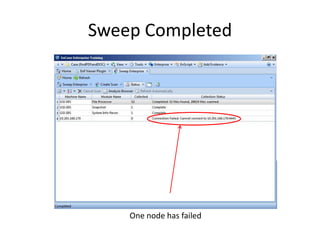
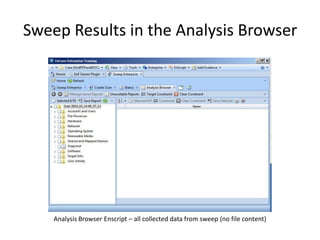
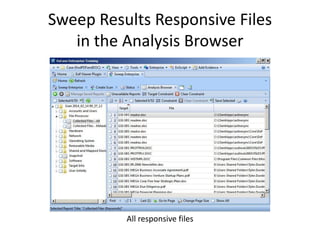
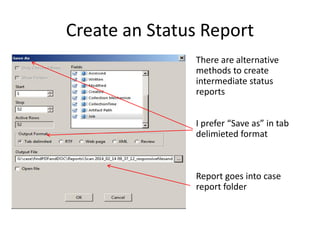
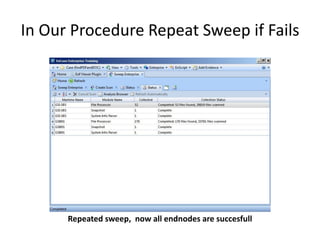
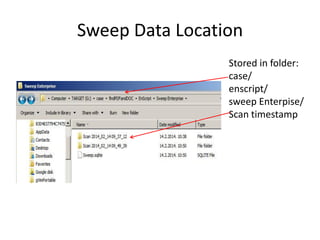
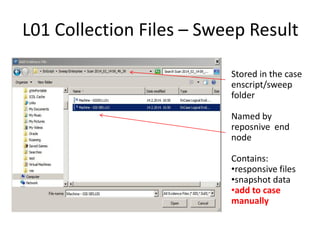
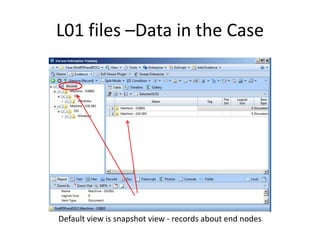
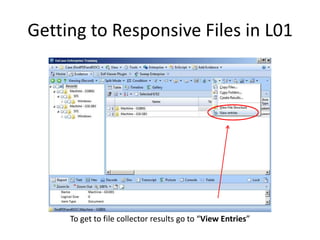
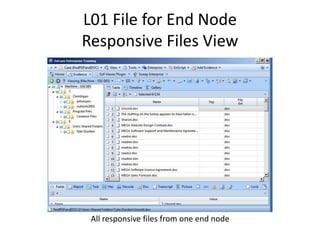
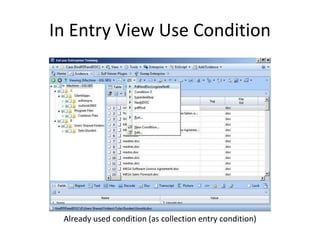
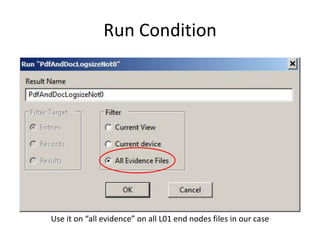
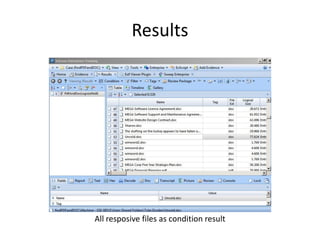
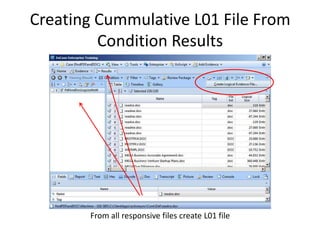
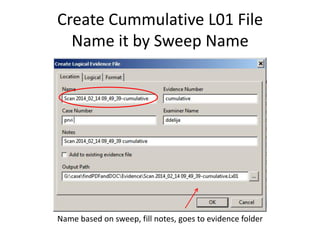
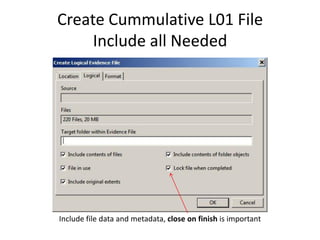
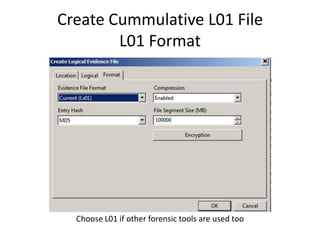
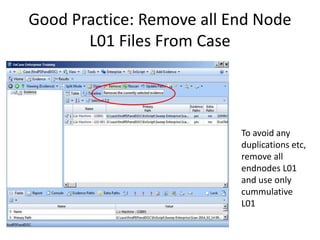
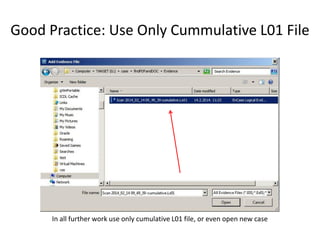
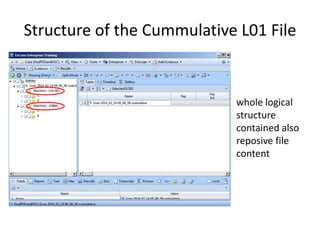
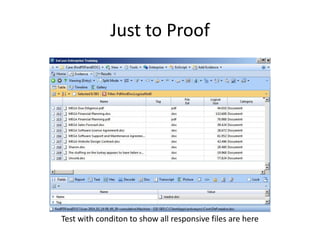
The document provides an overview of the basic steps for conducting an ediscovery collection using Guidance Software's EnCase Enterprise v7. It describes installing the required EnCase Enterprise components like the SAFE, Examiner and Servlets. It then outlines how to open a new case, define the target nodes, create a collection sweep to retrieve files and metadata based on conditions, and handle the sweep results. The summary provides the essential workflow and technical components involved in performing a foundational EnCase Enterprise collection.