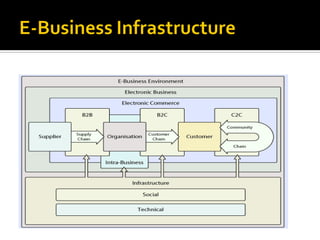
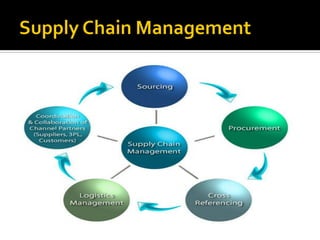
The video outlines the essentials of e-business and e-commerce, including fundamentals, infrastructure, and management practices. Key points include the importance of user experience, e-commerce strategy, security, and customer relationship management, as well as the benefits of e-marketing. It also addresses the rapid growth and challenges in mobile commerce, emphasizing the need for adaptive strategies in the evolving digital landscape.