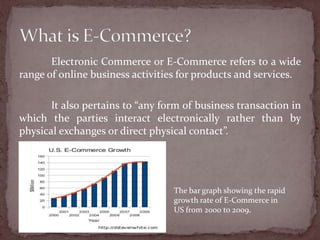
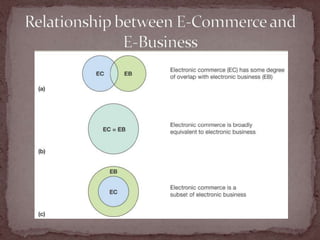
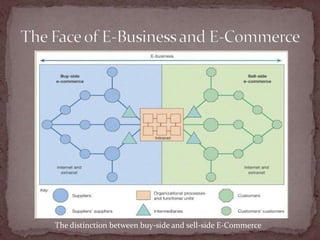
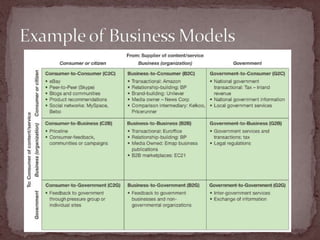
This document discusses the importance of e-business and e-commerce in today's economy, emphasizing its role in enhancing business strategies through technology. It covers various aspects of e-commerce, including buy-side and sell-side transactions, customer relationship management, and the rise of mobile commerce. The presentation also highlights best practices for online shopping experiences and the evolving landscape of electronic communication in business.