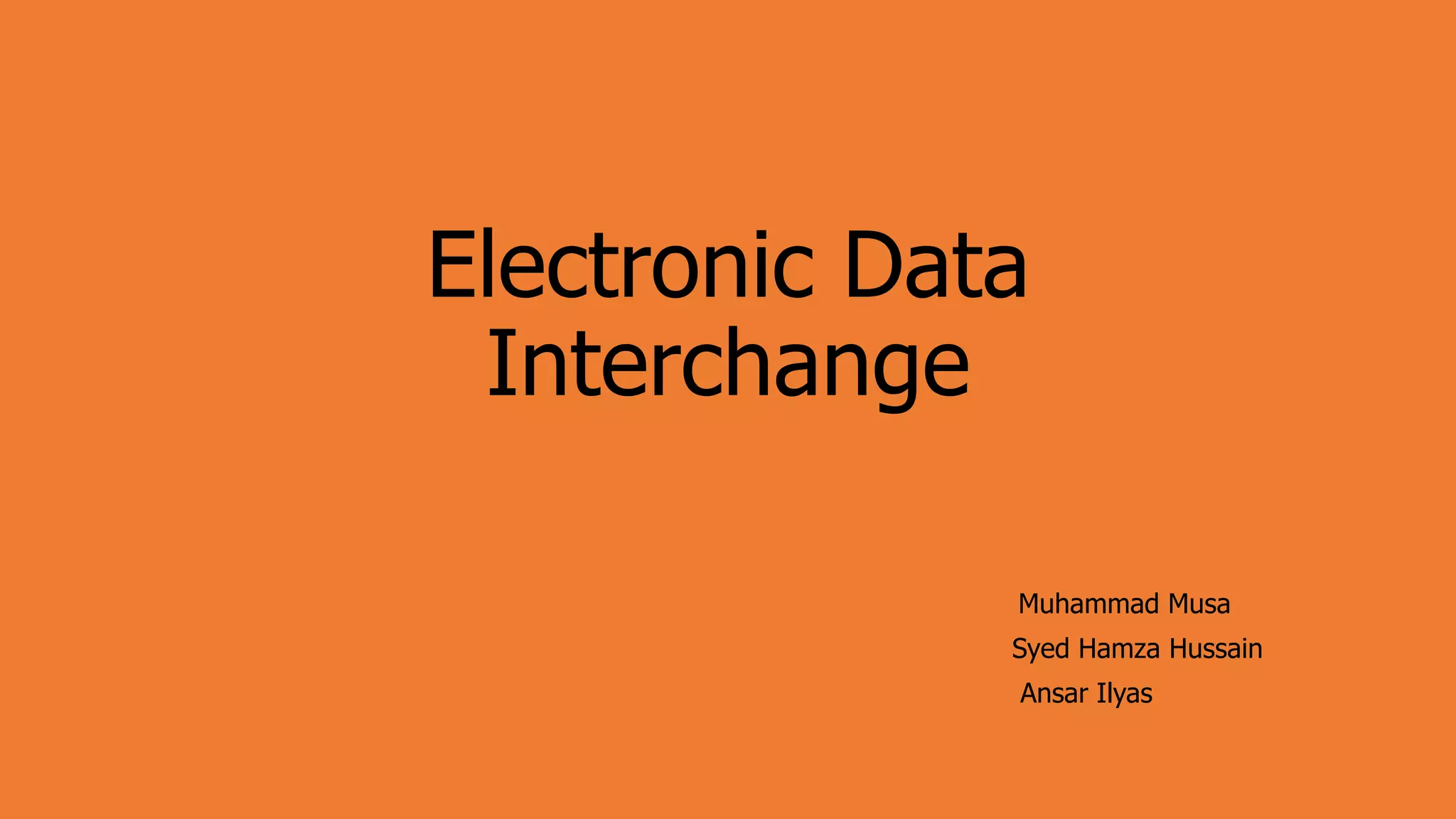
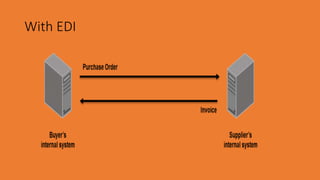
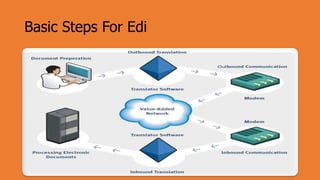
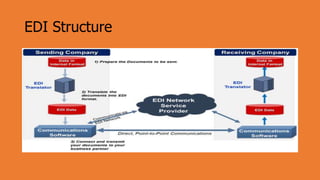
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) allows companies to exchange standard business documents like purchase orders and invoices in electronic format without manual intervention. EDI transactions are faster and more accurate than paper processes. EDI involves preparing data, translating it using standard formats, and transmitting documents electronically using a value-added network. While the initial costs are high, EDI can improve productivity and accuracy while reducing errors and paperwork between organizations.