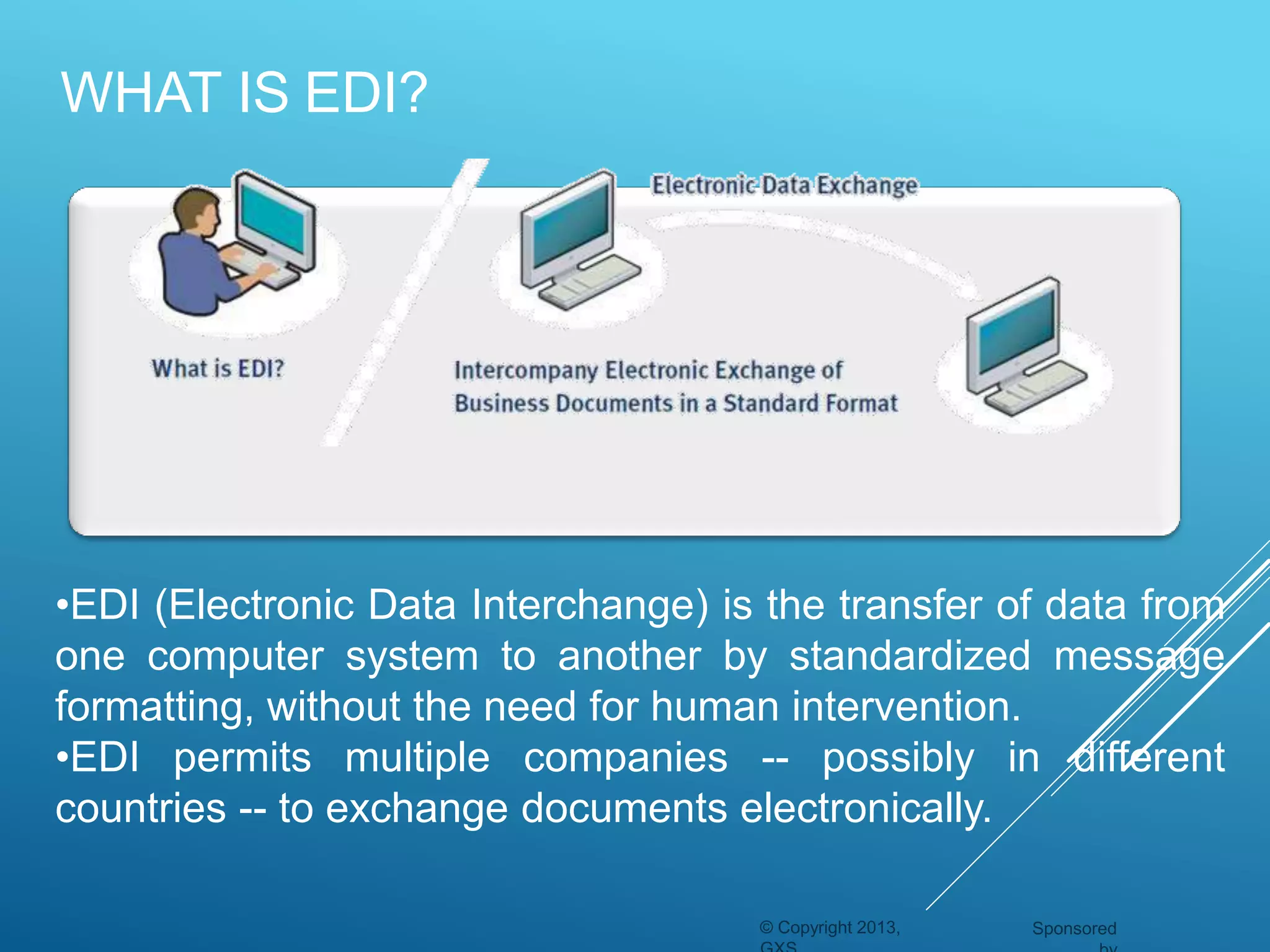
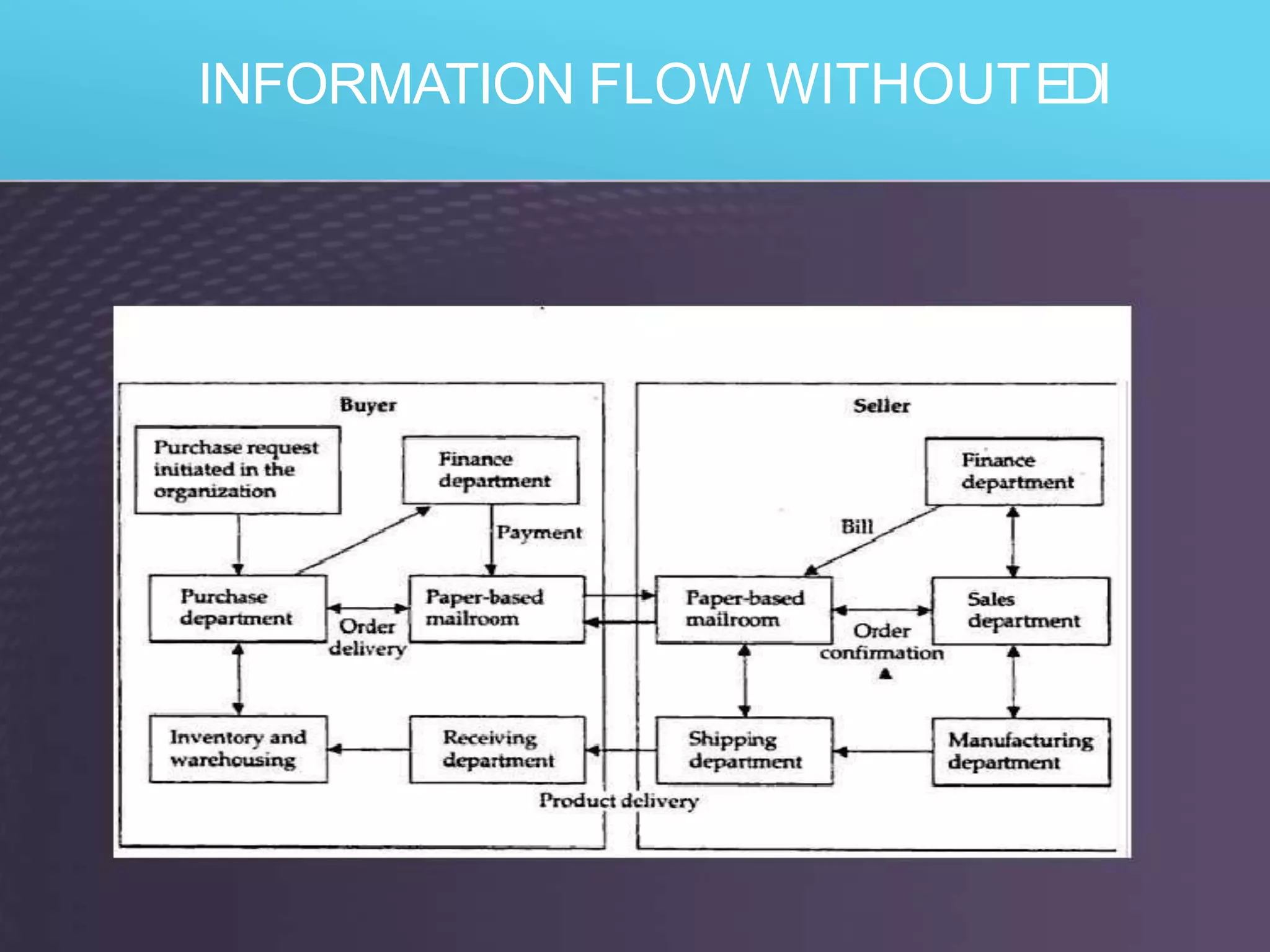
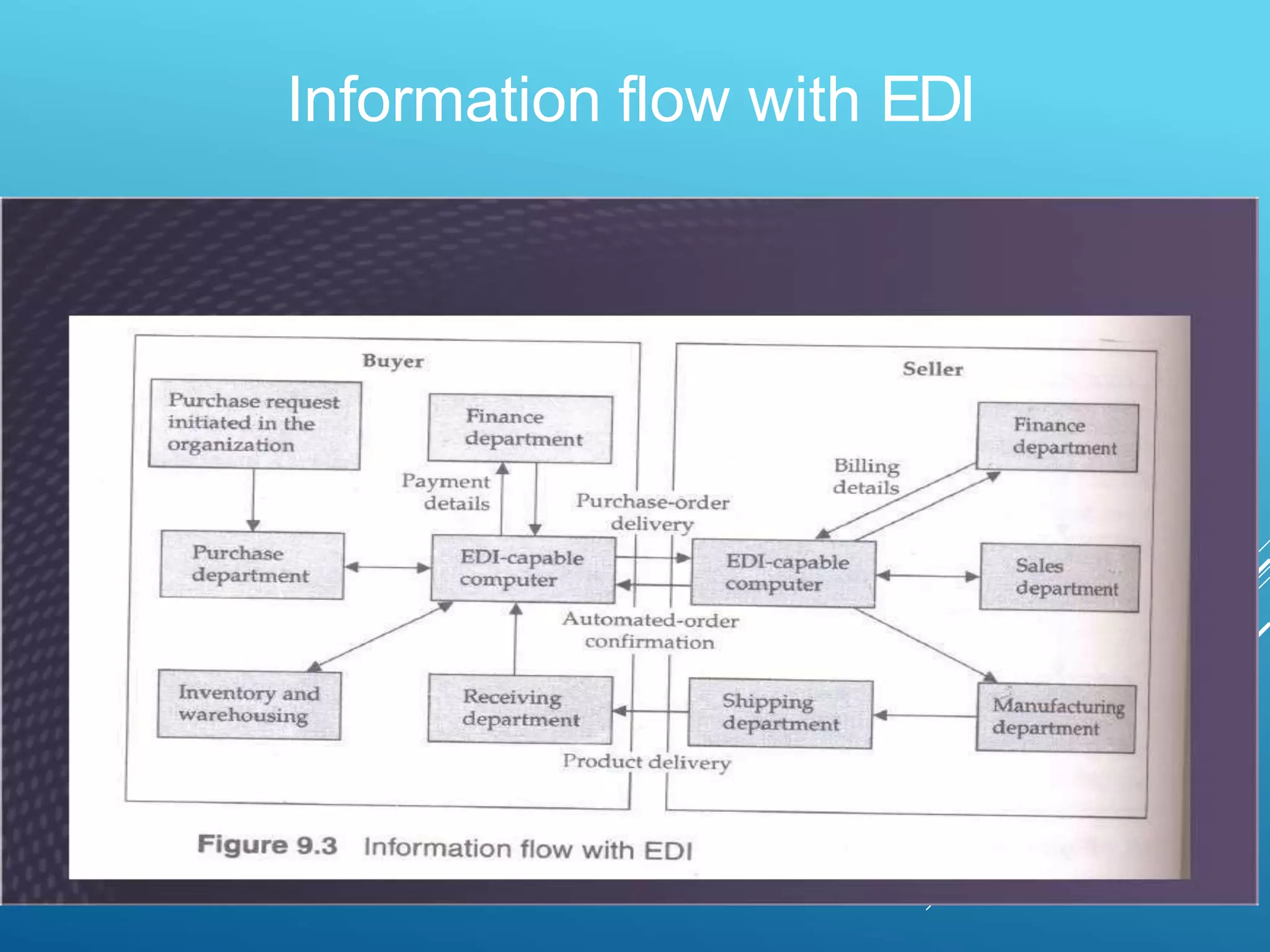
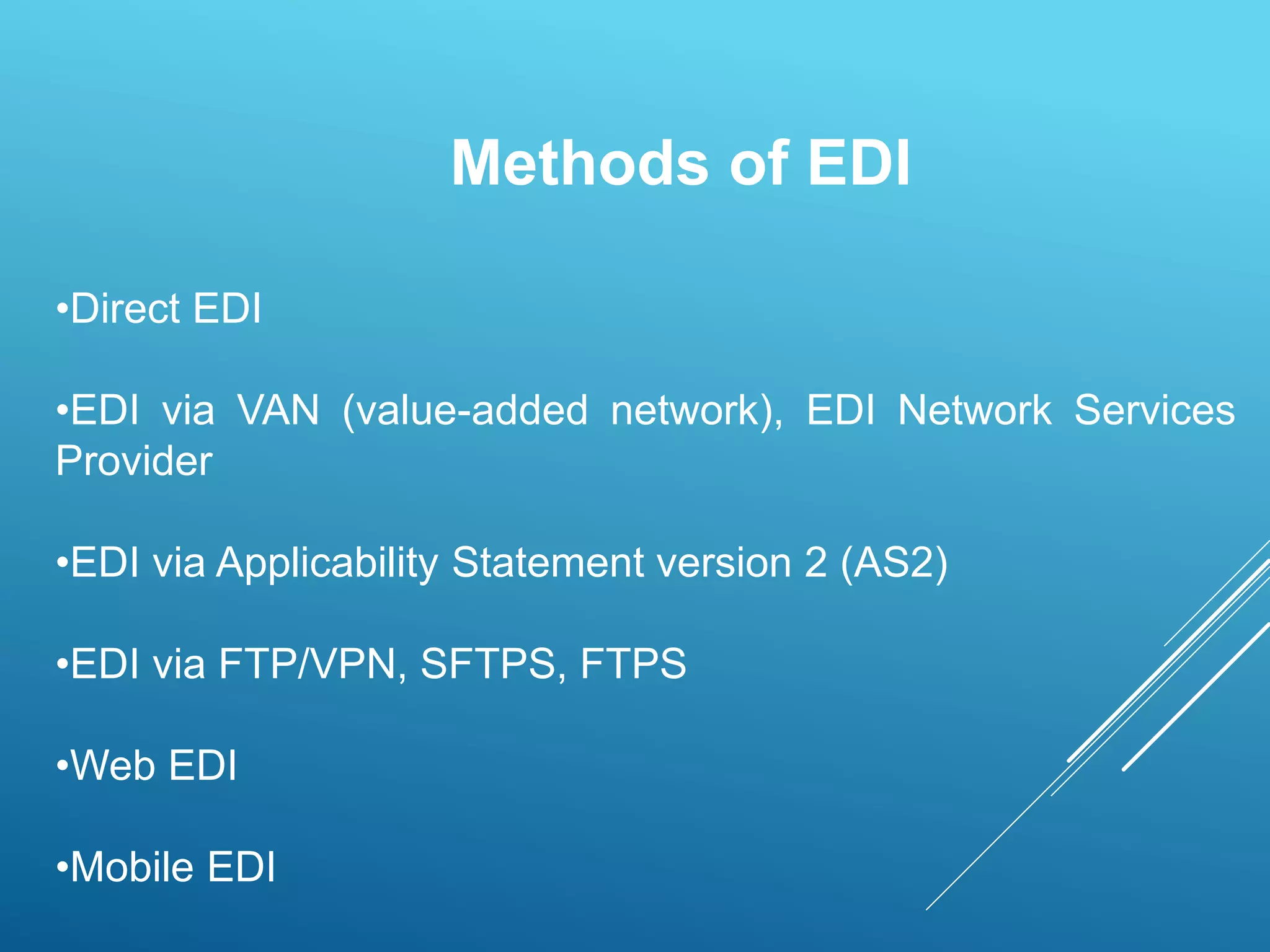
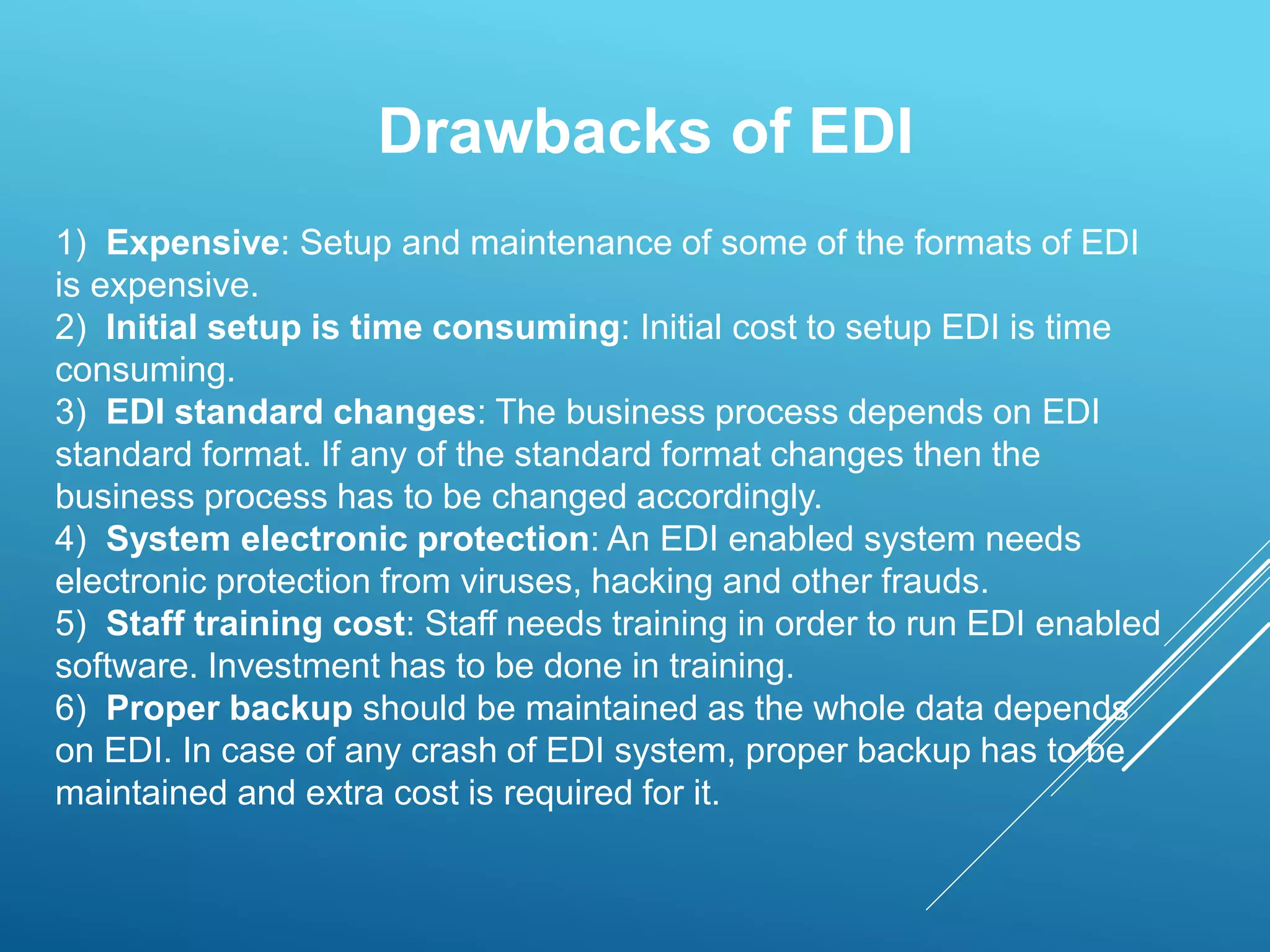
EDI is the electronic transfer of standardized business documents between computer systems without human intervention. It allows companies to exchange purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other documents electronically. The key benefits of EDI are more efficient transmission of information, automated data entry, receipt verification, data validation, lower costs, faster processing, and strengthened business relationships. However, initial setup and maintenance of EDI systems can be expensive and time-consuming.