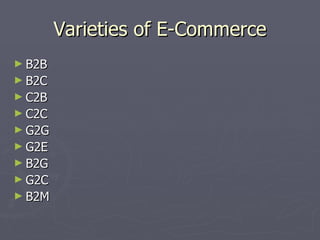
E-business involves automating business processes electronically and includes e-commerce transactions. It provides benefits like reduced costs, improved capabilities, communication, control, and customer service. E-business technologies empower employees, customers, suppliers, distributors, and vendors. There are various models of e-commerce like business-to-business, business-to-consumer, and consumer-to-consumer. Effective e-business requires appropriate hardware, software, and an internet-based infrastructure to connect the supply chain.