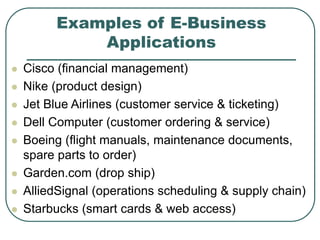
This document defines key terms related to e-business and e-commerce. It discusses how e-business involves conducting business processes over computer networks for areas like production, customers, and internal management. E-commerce specifically refers to transactions that transfer ownership or rights to use goods/services. The document provides examples of how automobile manufacturers and other companies have applied e-business strategies. It also outlines various models of e-commerce and potential members of e-commerce supply chains.