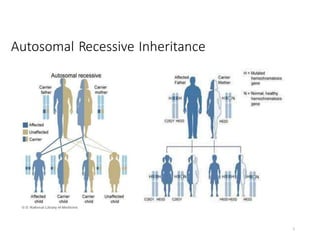
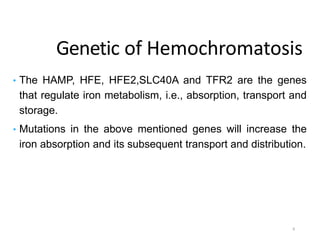
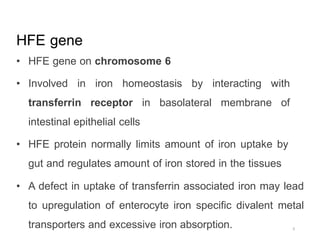
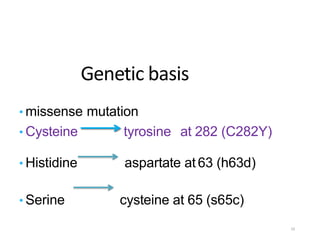
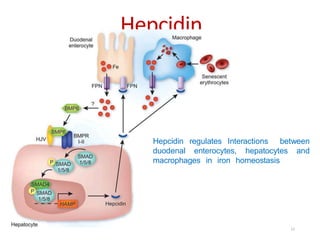
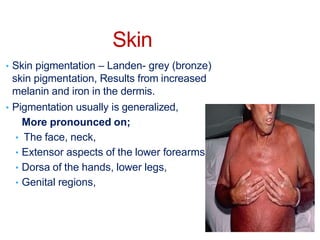
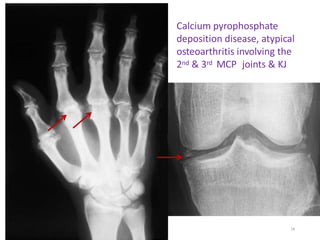
Genetic hemochromatosis is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by excessive iron absorption due to mutations in the HFE gene, leading to organ toxicity primarily affecting the liver, pancreas, and heart. The condition is most prevalent among Caucasians, with symptoms including liver dysfunction, skin pigmentation changes, diabetes, and arthritis. Screening and early phlebotomy treatment are critical for effective management, reducing the risk of complications such as cirrhosis and diabetes.