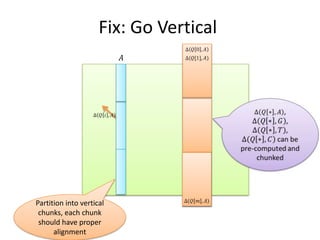
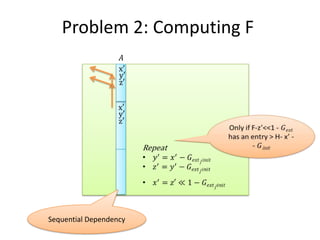
This document discusses using SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) instructions to parallelize dynamic programming algorithms. It provides an example of how a SIMD register can execute the same operation on multiple data elements in parallel. It also describes how to partition the dynamic programming problem into properly aligned chunks that can be processed simultaneously using SIMD to improve performance. Boundary conditions and dependencies between chunks are identified as challenges to be addressed for an effective parallel implementation.


![Edit Distance between Strings
Q
D
Edit distance
between Q[1..j]
and D[1..i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicprogrammingforsimd-120725071858-phpapp01/85/Dynamic-programming-for-simd-3-320.jpg)