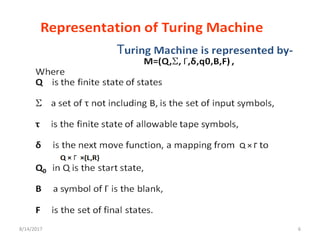
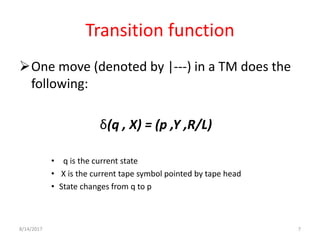
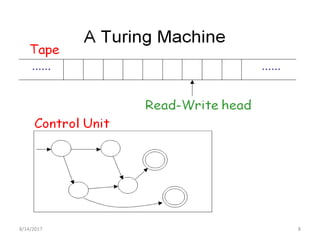
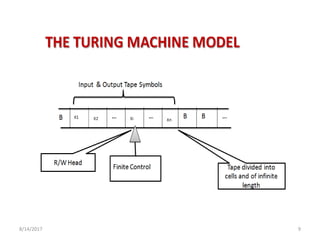
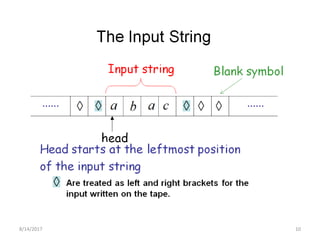
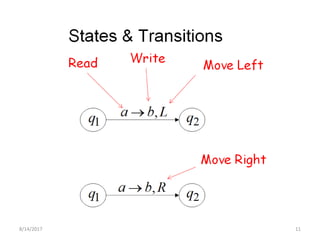
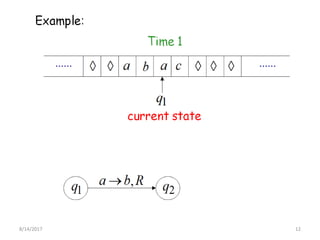
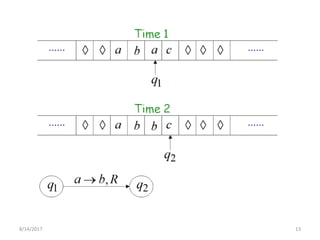
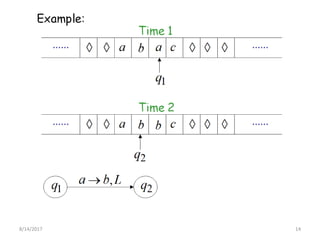
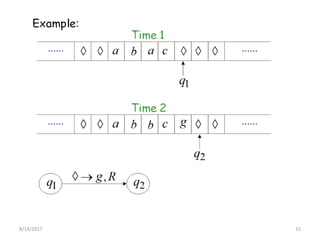
The presentation introduces Turing machines, which were conceived by Alan Turing in 1936 to model computation. A Turing machine is a mathematical model of a computer consisting of a finite state machine with an infinite tape and tape head that can read, write, and move left or right on the tape. It accepts input strings by entering an accepting state. The presentation then defines Turing machines and describes their transition functions and how a universal Turing machine can simulate any other Turing machine. In closing, properties of Turing machines are noted, including their ability to recognize languages generated by phrase-structure grammars.