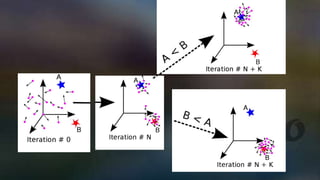
This document discusses particle swarm optimization (PSO), which is an optimization technique inspired by swarm intelligence and the social behavior of bird flocking or fish schooling. PSO uses a population of candidate solutions called particles that fly through the problem hyperspace, with each particle adjusting its position based on its own experience and the experience of neighboring particles. The algorithm iteratively improves the particles' positions to locate the best solution based on fitness evaluations.











![Each particle tries to modify its current position and velocity according to the distance between its
current position and pbest, and the distance between its current position and gbest.
Current Position[n+1] = Current Position [n] + v[n+1]
current position[n+1]: position of particle at n+1th
iteration
current position[n]: position of particle at nth iteration
v[n+1]: particle velocity at n+1th iteration
vn+1: Velocity of particle at n+1 th iteration
Vn : Velocity of particle at nth iteration
c1 : acceleration factor related to gbest
c2 : acceleration factor related to lbest
rand1( ): random number between 0 and 1
rand2( ): random number between 0 and 1
gbest: gbest position of swarm
pbest: pbest position of particle
21( )*( CurrentPosition ) 2( )*( CurrentPositionn n1 1 best,n best,n )randv v c rand p c gnn ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationai-150708073105-lva1-app6891/85/Particle-Swarm-Optimization-12-320.jpg)