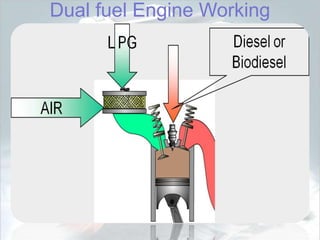
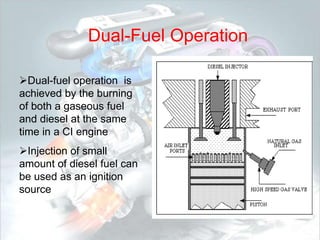
This document discusses dual fuel engines. It begins with an introduction explaining that dual fuel engines use a gaseous fuel inducted into the engine cylinder along with air, and a small amount of diesel fuel is injected as a pilot fuel to ignite the air-gas mixture. It then discusses factors that affect combustion in dual fuel engines like pilot fuel quantity and injection timing. The document outlines advantages of dual fuel engines such as reduced emissions and lower operating costs compared to diesel or natural gas engines. It concludes that dual fuel engines can substitute up to 70% of diesel fuel with a gaseous fuel like natural gas.