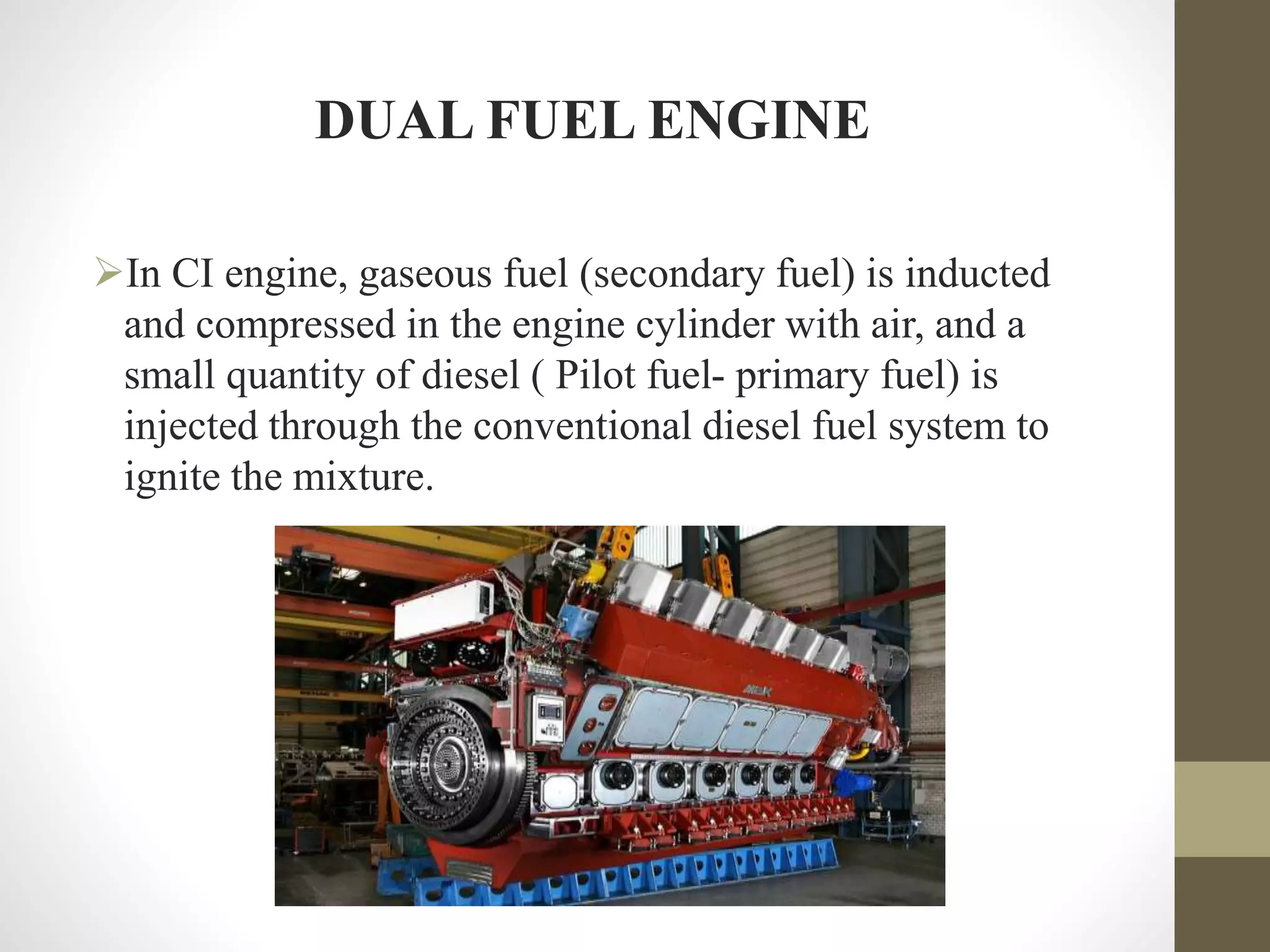
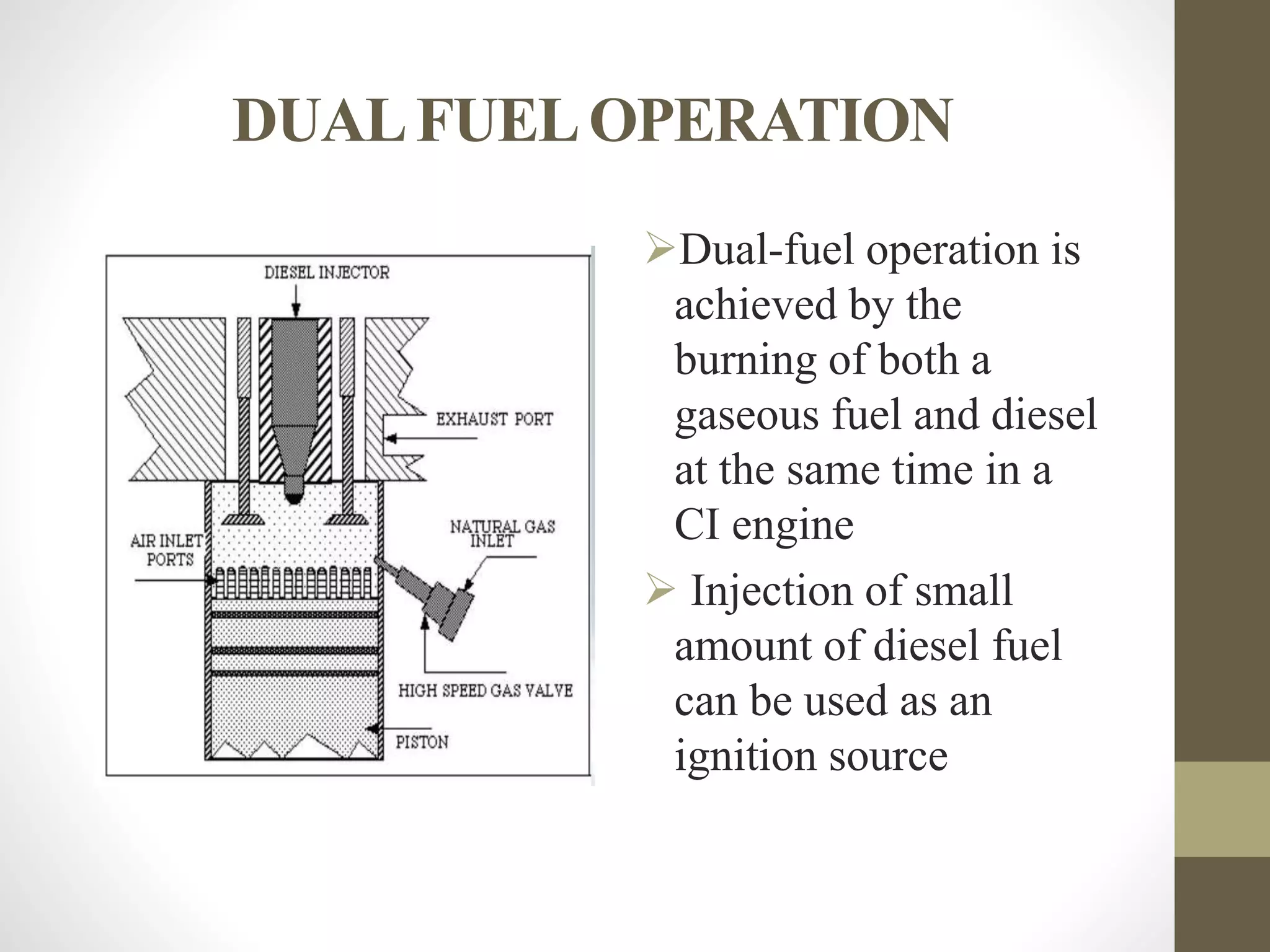
The document discusses dual fuel engines. It begins with an introduction that explains dual fuel engines use a gaseous fuel that is inducted and compressed in the cylinder along with air. A small amount of liquid fuel (pilot fuel) is then injected to ignite the gaseous fuel-air mixture. The working principle and factors affecting performance are then covered. Advantages of dual fuel engines include lower emissions and operating costs compared to diesel engines.