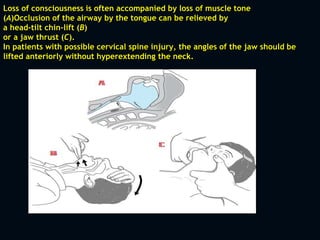
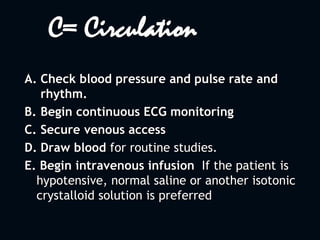
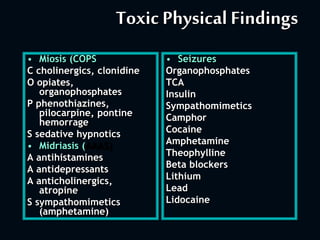
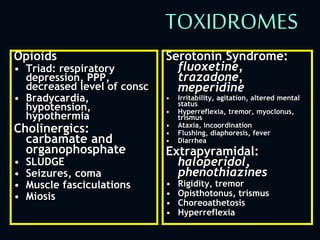
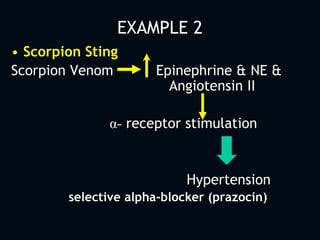
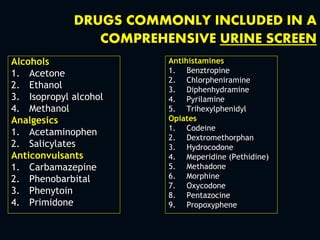
1. The initial management of all poisoned patients should be similar and focus on stabilization, including maintaining the ABCDEs. Airway patency, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure should be assessed and treated.
2. Definitive care involves identifying the toxic agent through history, physical exam including vital signs and toxic syndromes, and initial investigations like toxicology screening and basic labs.
3. Management then focuses on decreasing further absorption, administering antidotes if available, enhancing elimination, and treating complications through supportive care.




























![Osmolal Gap
OG = (measured serum osmolality) –
(calculated osmlality)
Calculated osmolality: [2(Na+) + (Glucose/18) +
(BUN/2.8)].
Normal Serum osmolality is 285-300 mOsm/kg.
Normal osmolal gap is 8-12 mOsm/kg.
Elevation due to presence of unmeasured, low-
molecular weight molecules that are osmotically
active:
Methanol
Ethylene glycol
Diuretics, such as glycerol, manitol, sorbitol
Isopropanol
Ethanol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generalmanagementofpoisoningtutorial-121219215110-phpapp02/85/Principles-of-Management-of-Acute-Poisoning-35-320.jpg)