I. This document discusses different methods of drug distribution in hospitals including individual prescription orders, floor stock systems, unit dose dispensing, and outpatient versus inpatient distribution.
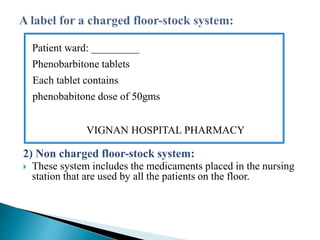
II. The main types of drug distribution systems covered are individual prescription ordering, complete floor stocking, a combination of the two, and unit dose dispensing.
III. Key aspects of each system like advantages, disadvantages, and procedures are summarized.