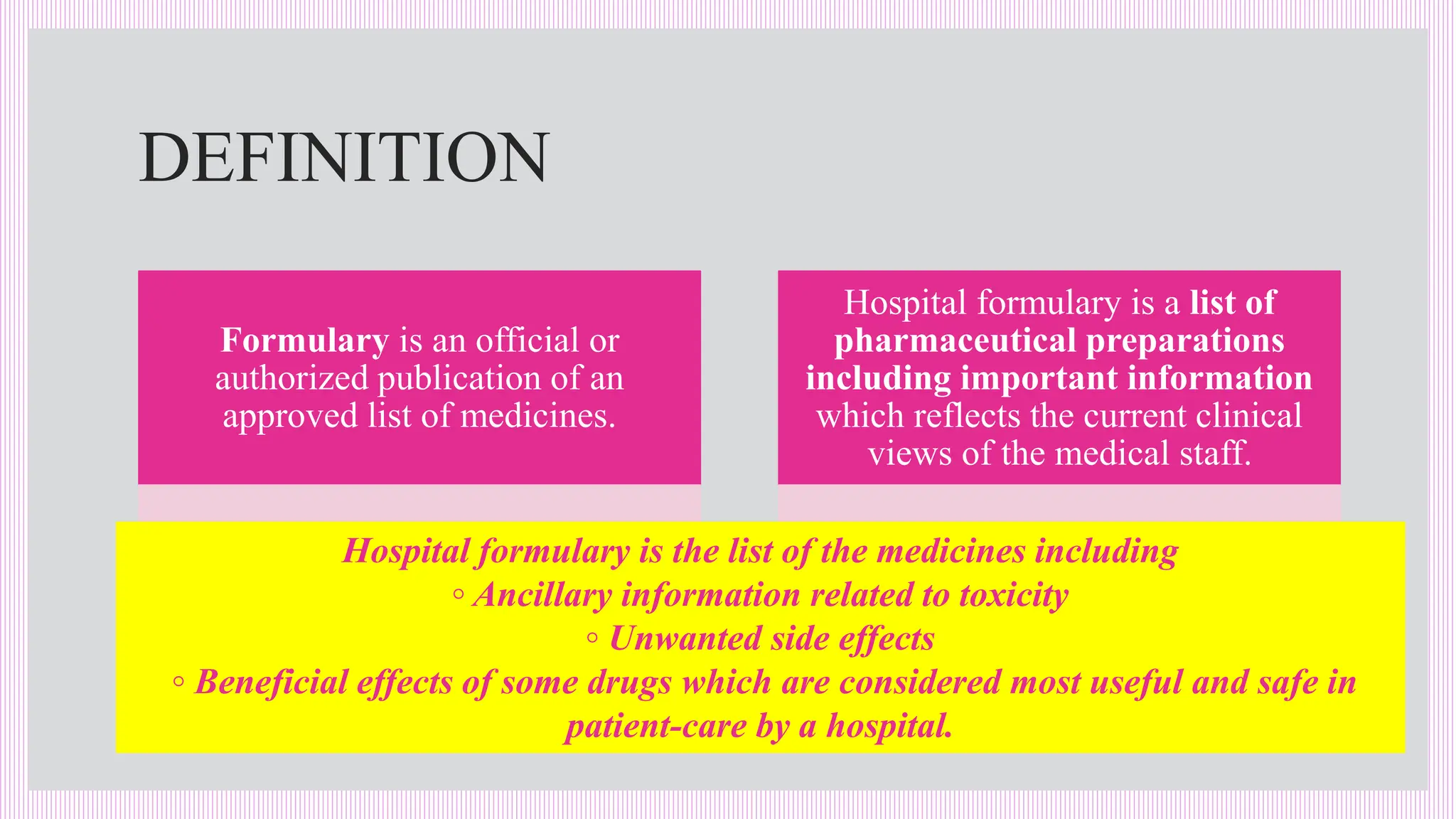
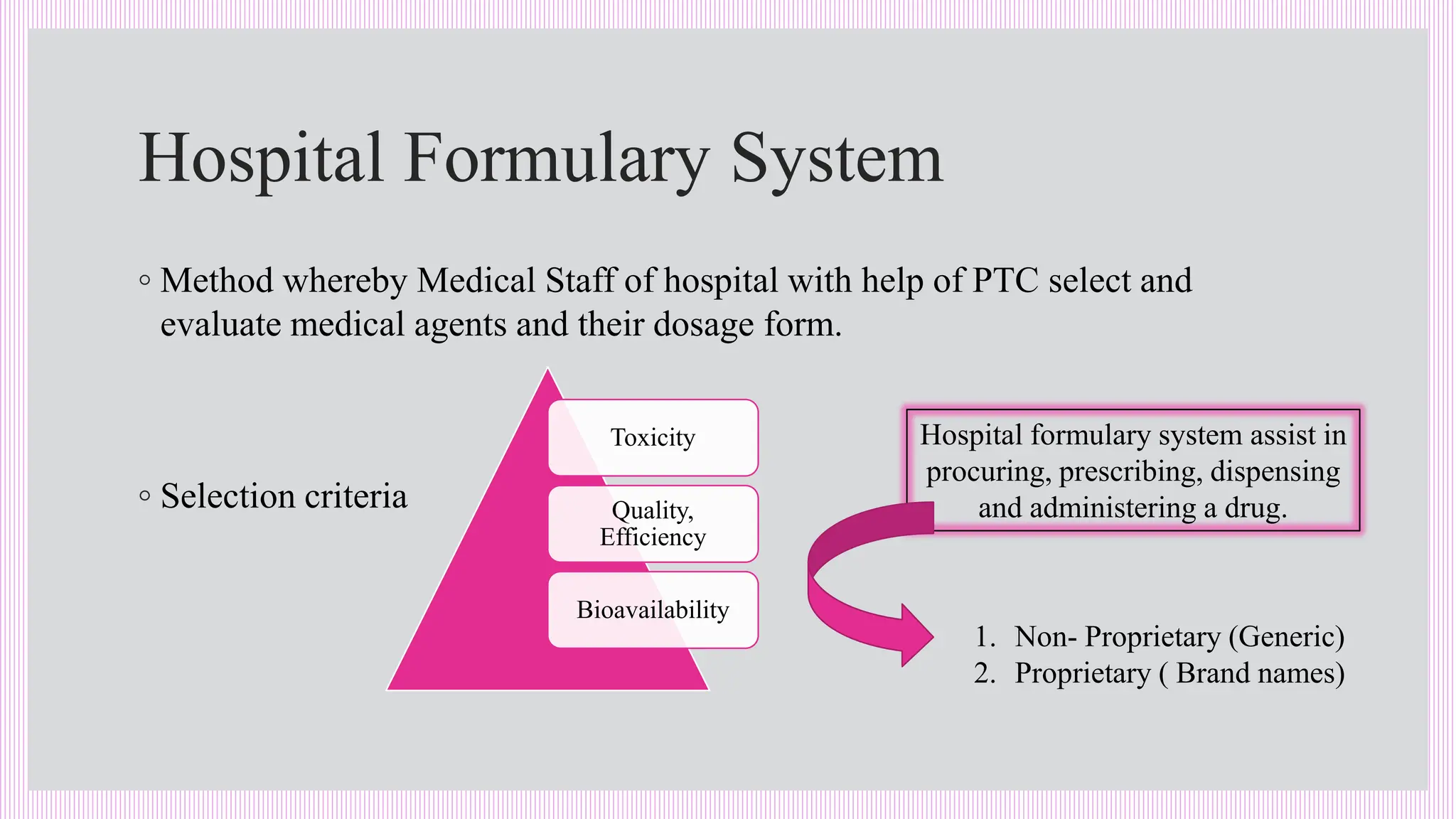
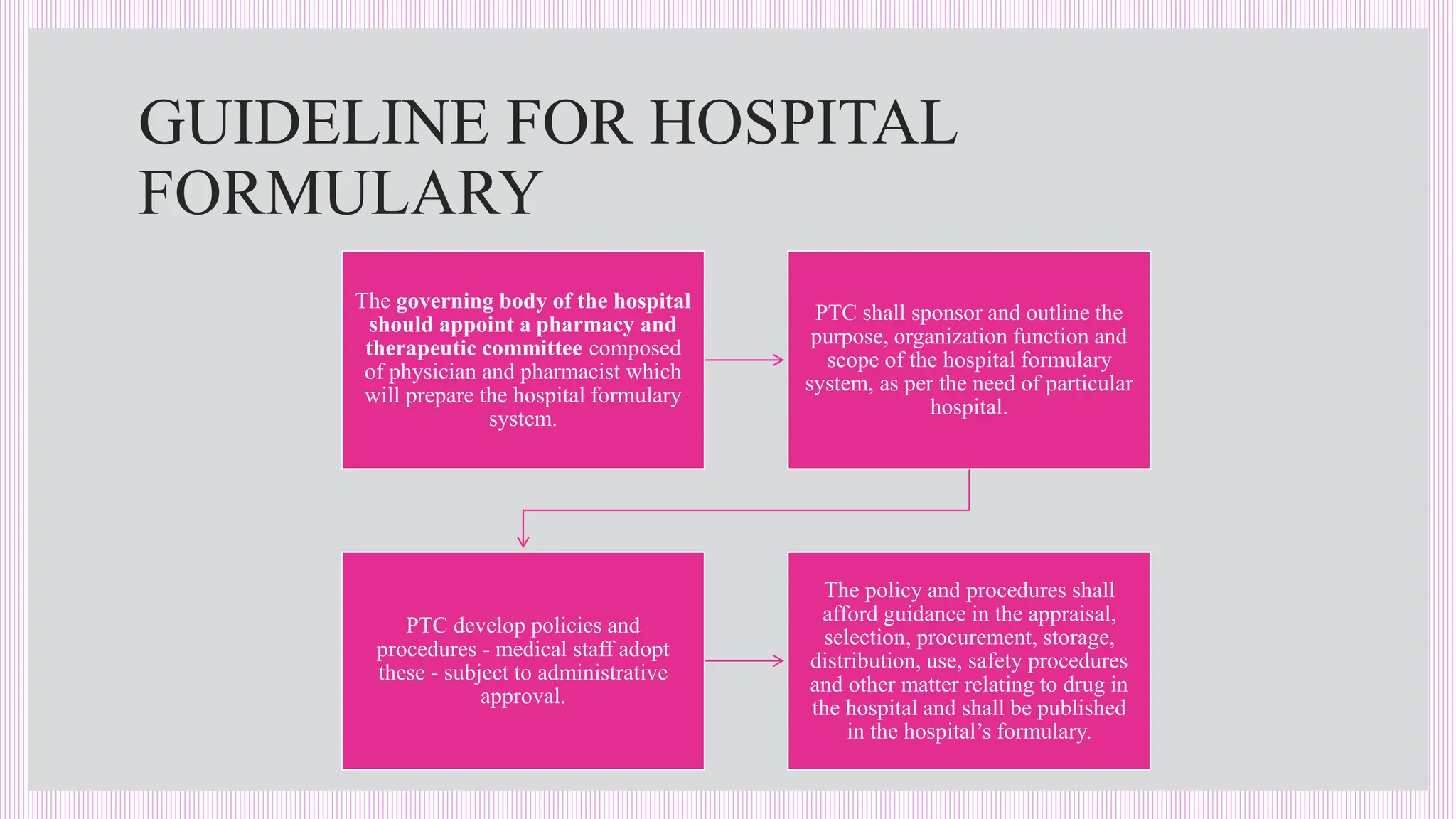
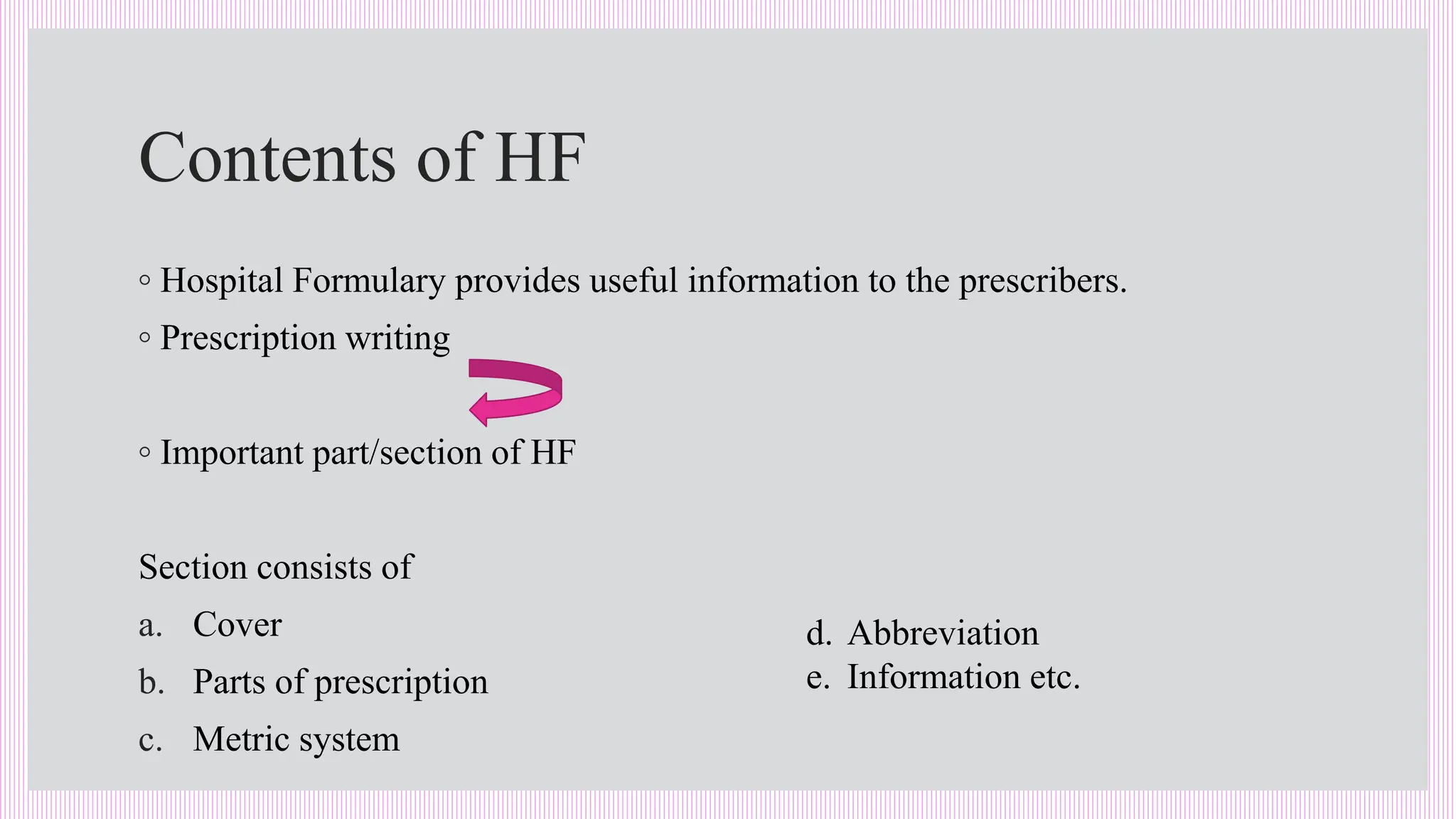
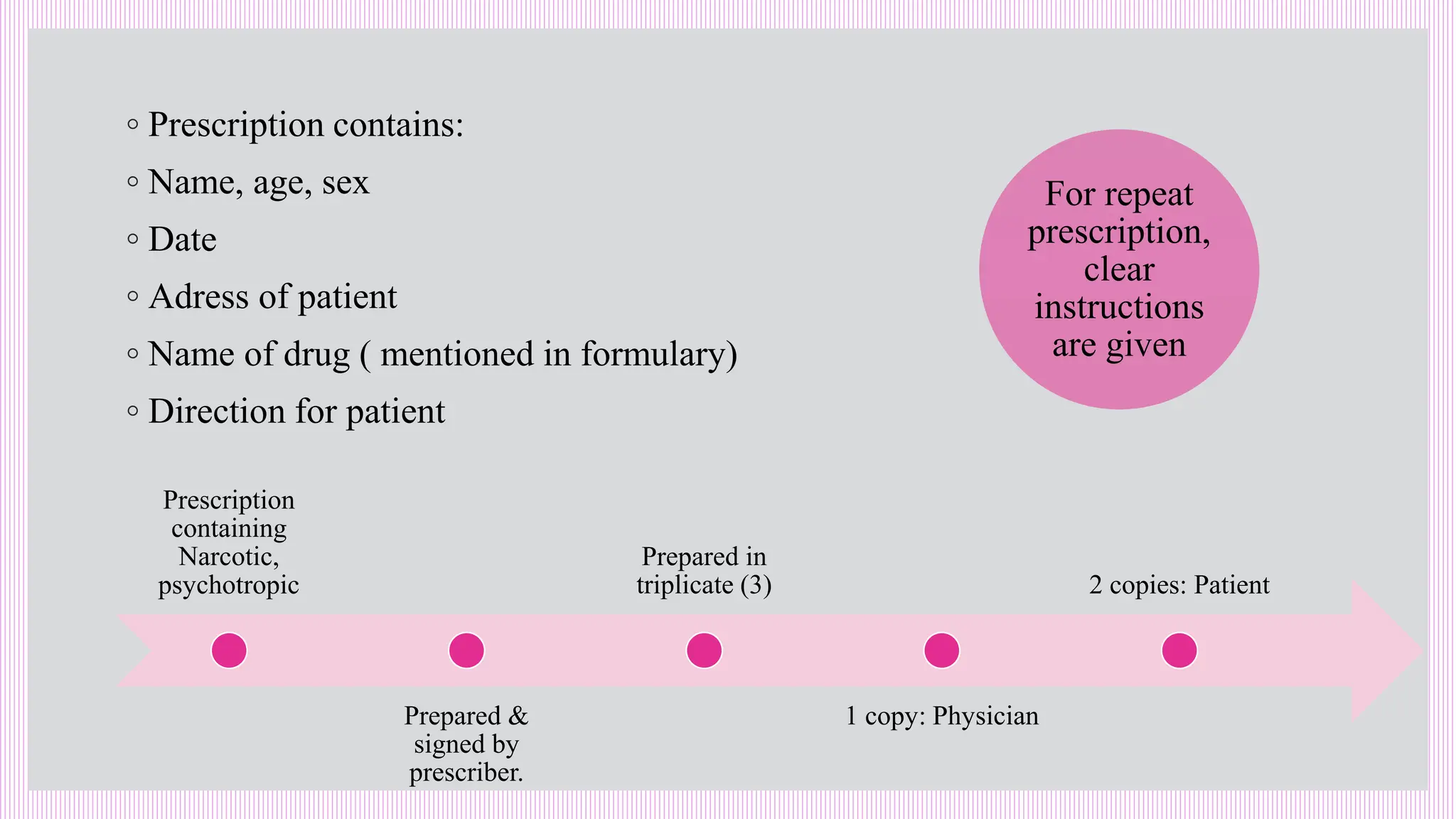
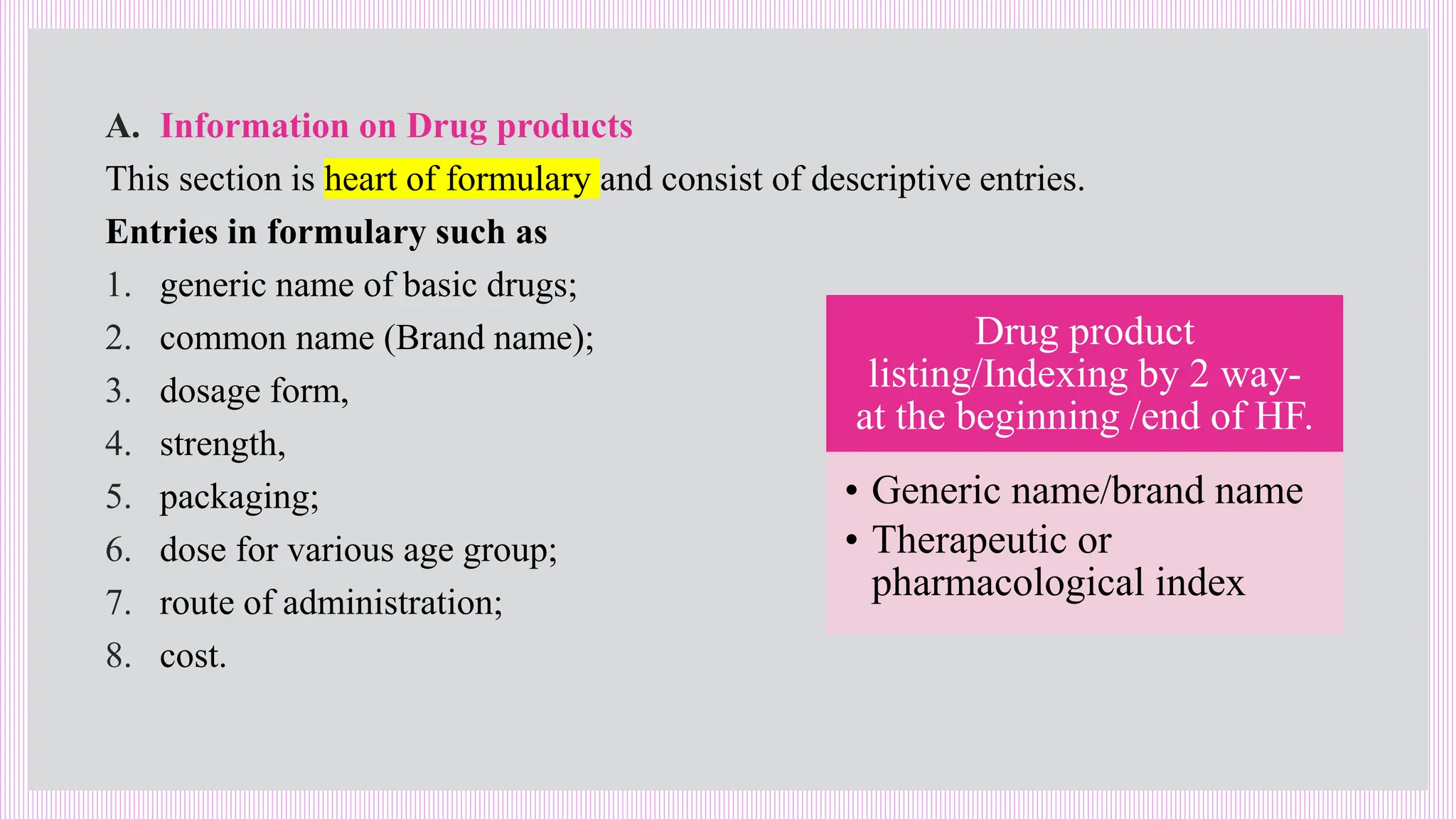
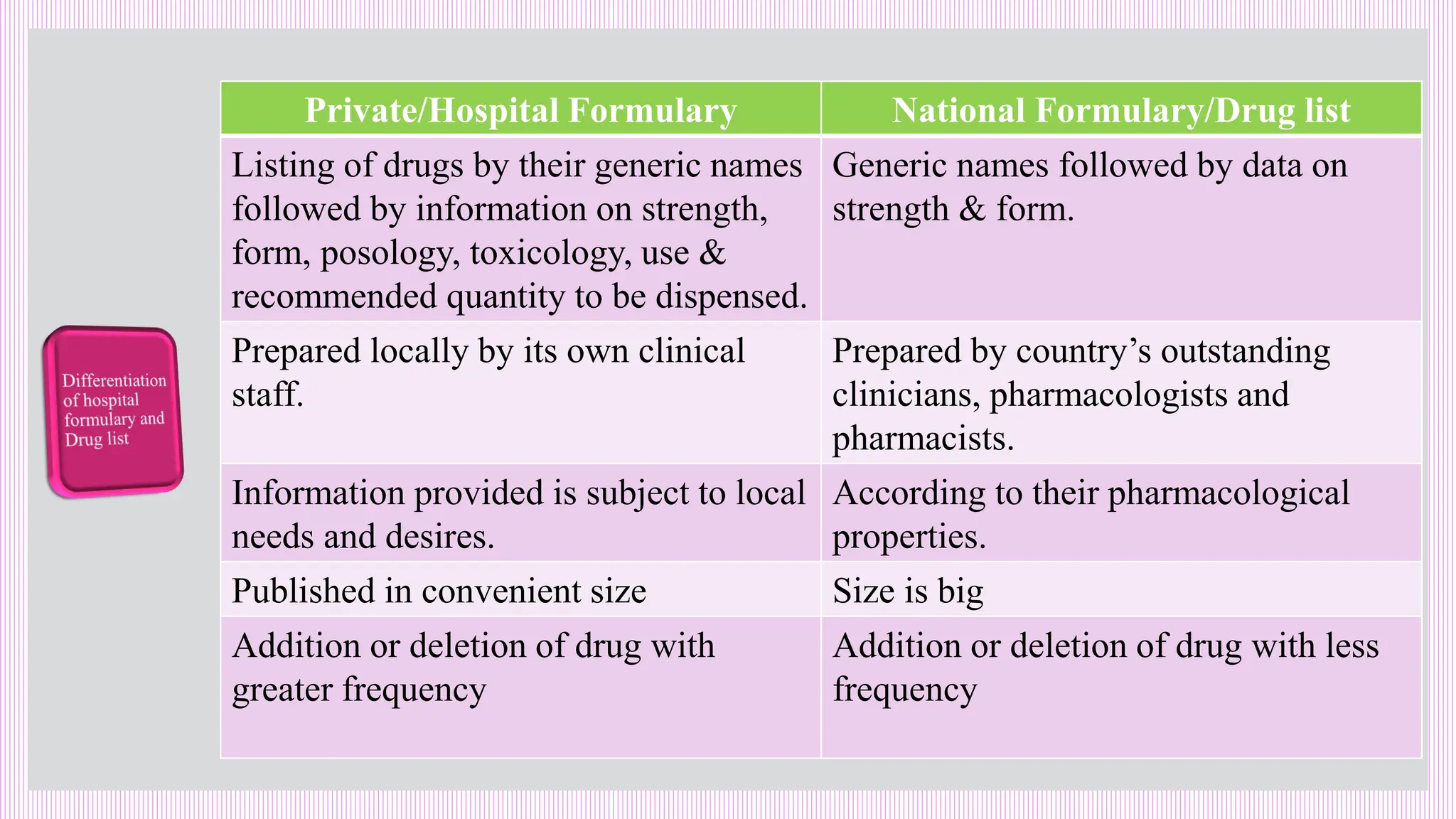
The hospital formulary is an official list of approved medicines that provides essential information on drug toxicity, side effects, and efficacy, established by a Pharmacy and Therapeutic Committee (PTC). It assists healthcare providers in effectively procuring, prescribing, and administering medications, while also promoting rational drug use and reducing costs. Regular revisions are necessary to adapt to new medical standards and practices, ensuring that only drugs with established therapeutic efficacy are included.