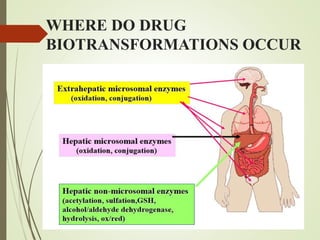
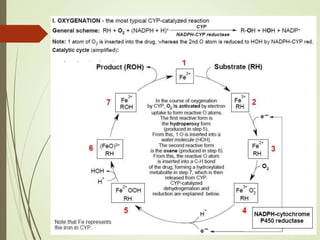
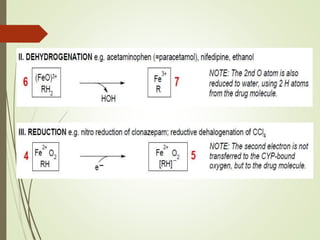
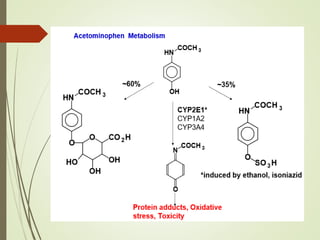
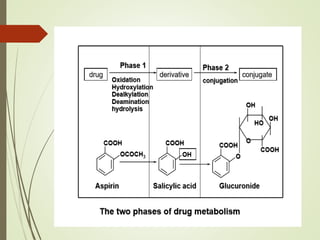
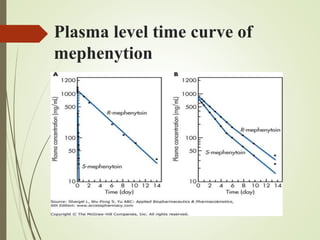
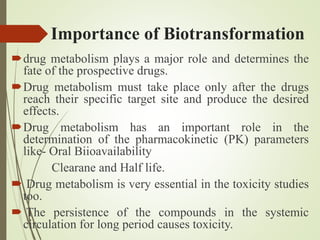
The document discusses drug biotransformation, the chemical conversion of drugs and xenobiotics within an organism, focusing on its role in altering drug activity and excretion. It outlines the processes of Phase I and Phase II reactions that facilitate drug metabolism and factors impacting these metabolic pathways. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of biotransformation in pharmacokinetics and toxicity studies.