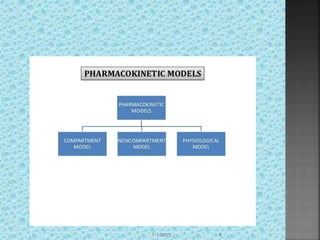
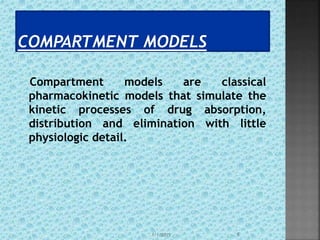
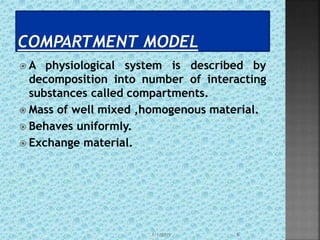
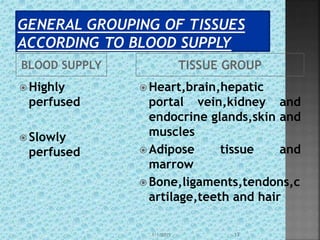
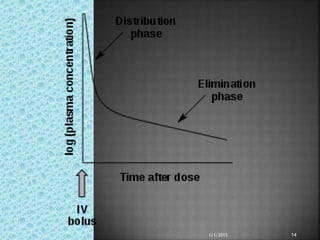
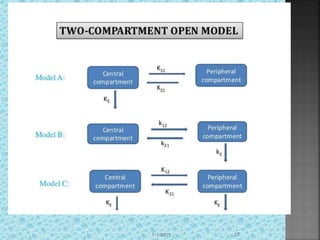
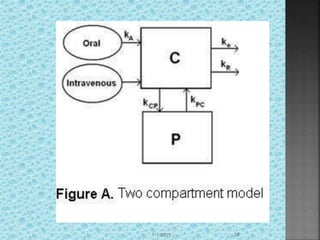
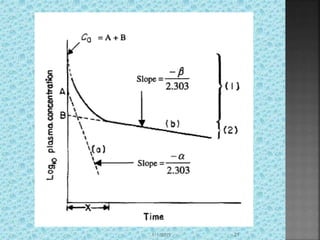
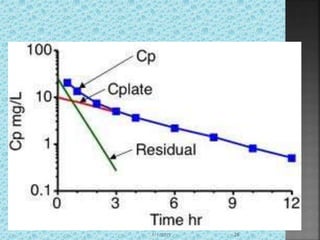
The document discusses two-compartment pharmacokinetic models. A two-compartment model describes the distribution and elimination of drugs in the body using two interconnected compartments - a central compartment representing blood and highly perfused tissues, and a peripheral compartment representing slowly perfused tissues. Parameters like volume of distribution, clearance, half-life and rate constants can be estimated from the biexponential decline in drug concentration observed following intravenous administration. Clinical applications including intravenous infusion and factors affecting pharmacokinetic parameters are also covered.























![D◦=VpCp
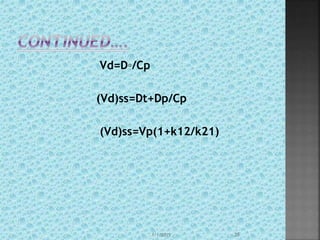
Vp=D◦/A+B
Vp=D◦/k[AUC]
1/1/2015 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twocompartmentmodel-150101132608-conversion-gate01/85/Two-compartment-model-33-320.jpg)
![ The rate of drug entry into the tissue
compartment from central compartment is
equal to the rate of drug exit from tissue
compartment into the central compartment
Dtk21=Dpk12
Dt=k12Dp/k21 [Dp=CpVp]
Dt=k12.CpVp/k21
1/1/2015 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twocompartmentmodel-150101132608-conversion-gate01/85/Two-compartment-model-34-320.jpg)



![ reduced drug clearance from the body
may increase AUC such that (Vp)ᵦ is either
reduced or unchanged depending on the
value of b.
(Vp)ᵦ=(Vd)area=Do/b[AUC]͚͚◦
Cl=Do/[AUC]͚◦
(Vd)ᵦ=Cl/b
(Vd)ᵦ=k.Vd/b
1/1/2015 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twocompartmentmodel-150101132608-conversion-gate01/85/Two-compartment-model-39-320.jpg)


/a-b
1/1/2015 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twocompartmentmodel-150101132608-conversion-gate01/85/Two-compartment-model-42-320.jpg)





![ Equation describing plasma drug
concentration:
Cp=R/Vpk[1-(k-b/a-b)e-ᵅᵗ_(a-k/a-b)e-
ᵇᵗ]
At steady state:
Css=R/Vpk
Infusion rate:
R=CssVpk
1/1/2015 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twocompartmentmodel-150101132608-conversion-gate01/85/Two-compartment-model-48-320.jpg)







