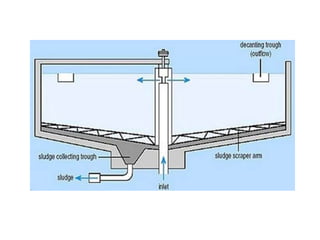
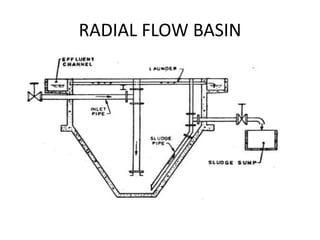
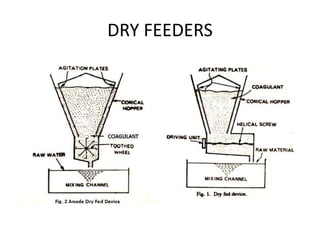
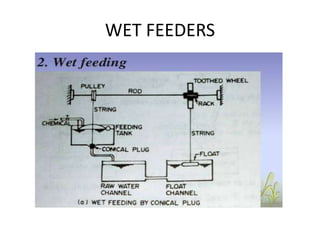
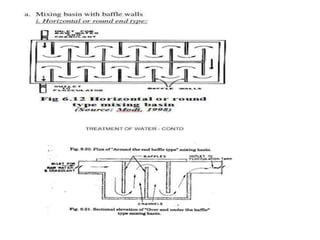
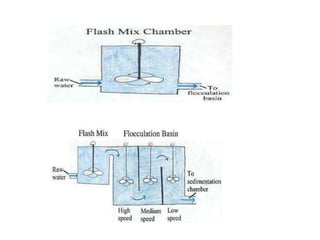
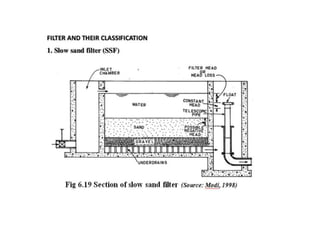
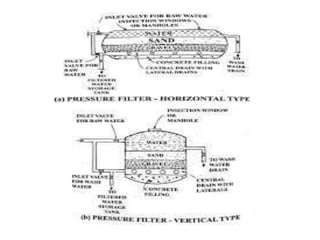
This document discusses various processes involved in water treatment, including sedimentation, coagulation, filtration, disinfection, and water softening. It also covers types of sedimentation and filtration tanks, factors affecting sedimentation, coagulation chemicals and feeders, and chlorination. Distribution systems are also summarized, including types of supply systems, layouts, and functions of service reservoirs. Key factors in reservoir sizing such as storage capacities are also outlined.