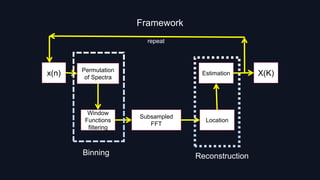
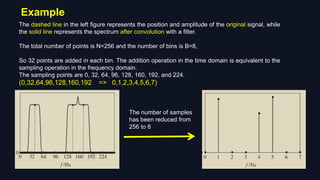
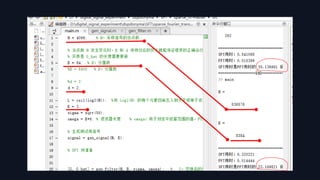
The Sparse Fourier Transform (SFT) algorithm provides an efficient method to compute the frequency spectrum of sparse signals. It takes advantage of signal sparsity by only calculating non-zero frequency components, greatly reducing computational load compared to the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). The SFT works by permuting the signal spectrum, filtering it using window functions, taking a subsampled FFT to locate non-zero frequencies, and then estimating their amplitudes. This allows it to handle much larger signals faster than the DFT, with applications in areas like signal processing, image compression, and machine learning.





![1. Choose a random σ, τ ∈ [n] with σ odd.
2. Define y = G · (Pσ,τ x), so yi = Gixσi+τ . Then supp(y) ⊆ supp(G) = [w]
3. Compute ˆzi = ˆyi(n/B) for i ∈ [B]. By Claim 3.7. this is the DFT of zi = ∑j=0
⌈w / B⌉−1 yi+jB .
4. Define the ”hash function” hσ : [n] → [B] by hσ (i) = round(σiB/n)
and the ”offset” oσ : [n] → [−n/(2B), n/(2B)] by oσ (i) = σi− hσ (i)(n/B).
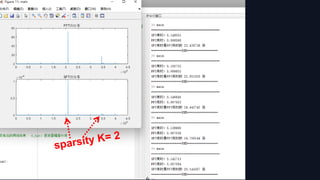
5. Location loops: let J contain the dk coordinates of maximum magnitude in ˆz.
Output I = {i ∈ [n] | hσ (i) ∈ J}, which has size dkn/B.
6. Estimation loops: for i ∈ I, estimate ˆxi as ˆx′i = ˆzhσ (i)ωτ i/ ˆGoσ (i)
Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donysimpleandpracticalalgorithmsft-230428033554-e0c59c81/85/DONY-Simple-and-Practical-Algorithm-sft-pptx-8-320.jpg)
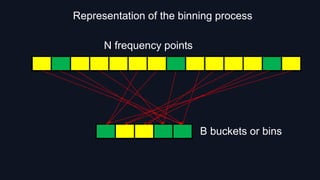
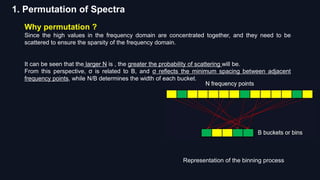
![1. Permutation of Spectrum:
MIT method of Permutation of Spectra: select a certain probability and permutate datas by the properties of DFT
1. DFT two properties:
Shifting property: if x1 (n) =x(n)WN
bn , X1 (k) = X(k+b) ;
if x2 (n) =x(n-b) , X2 (k) = WN
bkX(k) ;
Scaling property: if x3 (n) =x (σn) , X2 (k ) = X(σ-1k) ;
(σσ-1 ) mod N =1 ,
σ-1 is the number-theoretic inverse of σ
The formula for the transform is (Pσ,τ
x)i = xσi+τ, which means that the i-th
element of the transformed vector is
equal to the element of x that is
located at position σi+τ. In other
words, the elements of x are
rearranged based on the values of σ
and τ.
Define the transform Pσ,τ such that,
given an n-dimensional vector x,
an integer σ that is invertible mod n,
and an integer τ ∈ [n] ,
The associated permutation on a vector
x is given by (Pσ,τ x)i = xσi+τ
(Pσ,τ x)i = xσi+τ
=>
2. The property that the selection of σ mainly follows :
This mainly illustrates the signal can be reconstructed and Pσ,τ
is a permutation of x.
In sum, we denote that p (n) = x(σn+τ) and P (σk) = X(k) WN
-τk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donysimpleandpracticalalgorithmsft-230428033554-e0c59c81/85/DONY-Simple-and-Practical-Algorithm-sft-pptx-9-320.jpg)






![3. Subsampled FFT:
To subsample the frequency domain X(k) to obtain all the maximum
value points with the same interval N/B:
Y(k) =P(k N/B) , k ∈ [0,B -1]
Nevertheless,It is not easy to directly operate in frequency domain.
Instead, we can accomplish this step by time domain aliasing.
Permutation of Spectra:
p (n) = x(σn+τ)
P (σk) = X(k) WN
-τk
As Frequency domain sampling
theorem said: Frequency domain
s am pl i ng c aus es peri odic
replication of the time domain
sequence. When the number of
sampling points in one period in
the frequency domain is greater
than or equal to the number of
points in the time domain
sequence, it will not cause time
domain aliasing. If this condition
is not satisfied, it will cause time
domain aliasing.
Firstly, we have a time-domain sequence p[n] with length j. We perform DTFT on it,
obtaining its frequency spectrum P(ejω).
Then, we sample the frequency spectrum with a period of B points to obtain Y[k] =
P(ejωk). Then, we perform IDFT on Y[k], obtaining y[n].
The formula represents the relationship between y[n] and p[n] after time
domain aliasing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donysimpleandpracticalalgorithmsft-230428033554-e0c59c81/85/DONY-Simple-and-Practical-Algorithm-sft-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![3. Subsampled FFT:
To subsample the frequency domain X(k) to obtain all the maximum
value points with the same interval N/B:
Y(k) =P(k N/B) , k ∈ [0,B -1]
Nevertheless,It is not easy to directly operate in frequency domain.
Instead, we can accomplish this step by time domain aliasing.
Therefore, after the time-domain aliasing of the signal, performing an FFT operation
with B points can obtain a frequency domain subsampled sequence that contains all
the maximum value points.
Permutation of Spectra:
p (n) = x(σn+τ)
P (σk) = X(k) WN
-τk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donysimpleandpracticalalgorithmsft-230428033554-e0c59c81/85/DONY-Simple-and-Practical-Algorithm-sft-pptx-19-320.jpg)

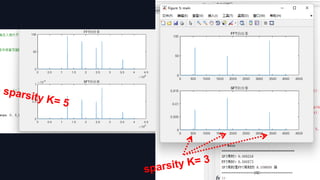
![4. Localization:
Firstly, the signal frequency sequence Z(k) obtained after
subsampling the FFT.
Select the coordinates of the top dK maximum values Z(ki) ,
i ∈[0 , dK-1], and put their frequency point k into set J.
Why we select dK coordinates
instead of K coordinates?
After spectrum permutation, filtering,
subsampling, and other operations, additional
frequency components are inevitably
generated. So selecting more coordinates
helps to identify which "bins" contain useful
signals and which "bins" contain useless
signals.
K : sparsity
d : a positive integer
used to determine
the computational
precision
Then obtain the J’s original frequency set through hash
inverse-mapping.
Ir ={ k∈ [0,N -1] | hσ(k) ∈J }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donysimpleandpracticalalgorithmsft-230428033554-e0c59c81/85/DONY-Simple-and-Practical-Algorithm-sft-pptx-22-320.jpg)
![5. Estimation:
The idea behind amplitude estimation :
dividing the value in each bin by the Gain of the filter to obtain an estimated value Xr(k),
Xr(k) means the amplitude corresponding to the frequency value obtained from each bin after inverse
mapping .
In the spectrum, two pieces of information are needed: frequency and amplitude. The previous step of
"locating" solves the former, determining which frequency components are actually being used, while
this step addresses the latter, namely, what is the amplitude of each frequency component.
X(k) = median( { Xr(k) | r ∈ {1,2, … ,L} } )
In each localization cycle, a set Ir is obtained : Ir ={ k∈ [0,N -1] | hσ(k) ∈J }
In L cycles,
for any coordinate k ∈ I = I1 ∪ I2 ........ ∪ IL,
if its frequency is greater than L/2, it is classified into the set I′, and set I′ contains all target frequency
point coordinates.
For each k ∈ I′, the median value of X(k) obtained from L cycles is taken as the final frequency value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donysimpleandpracticalalgorithmsft-230428033554-e0c59c81/85/DONY-Simple-and-Practical-Algorithm-sft-pptx-23-320.jpg)



![马悦淇
Dony Ma
Electronic and Information Engineering
School of Computer Science and Engineering
Faculty of Innovation Engineering
Macau University of Science and Technology
2009853li011004@student.must.edu.mo
1.https://oi-wiki.org/math/number-theory/basic/
2.https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-cn/数论
3.《一切皆是映射:代码的本质》Hash算法
4.https://github.com/bernielampe1/sparse_fft
5.Hassanieh H, Indyk P, Katabi D, et al. Simple and practical algorithm for sparse fourier transform[C] ∥Proceedings of
Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms. [ S. l. ]: ACM, 2012: 1183 1194.
6.http://spiral.net/index.html
7.Hassanieh H, Indyk P, Katabi D, et al. Nearly optimalsparse fourier transform[C] ∥Proceedings of Annual ACM
Symposium on Theory of Computing. [S.l. ]: ACM, 2012:563 577.
8.http://groups.csail.mit.edu/netmit/sFFT/ENC_SFFT.pdf
9.http://groups.csail.mit.edu/netmit/sFFT/Documentation.pdf
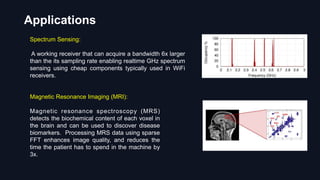
10.http://groups.csail.mit.edu/netmit/sFFT/applications.html
11.https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/sasp/Discrete_Time_Fourier_Transform.html
12.Sparse Fast Fourier Transform Code Documentation (SFFT 1.0 and 2.0)
13.陶然, 刘升恒, 张果, 等. 一种利用稀疏傅里叶变换计算外 辐 射 源 雷 达 互 模 糊 函 数 的 方 法](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donysimpleandpracticalalgorithmsft-230428033554-e0c59c81/85/DONY-Simple-and-Practical-Algorithm-sft-pptx-33-320.jpg)