This document provides an overview of the Domain Name System (DNS). It describes how DNS uses domain names to map to IP addresses in a hierarchical structure. Key points include:
- DNS allows users to use domain names like "example.com" instead of numeric IP addresses for easier identification of internet hosts.
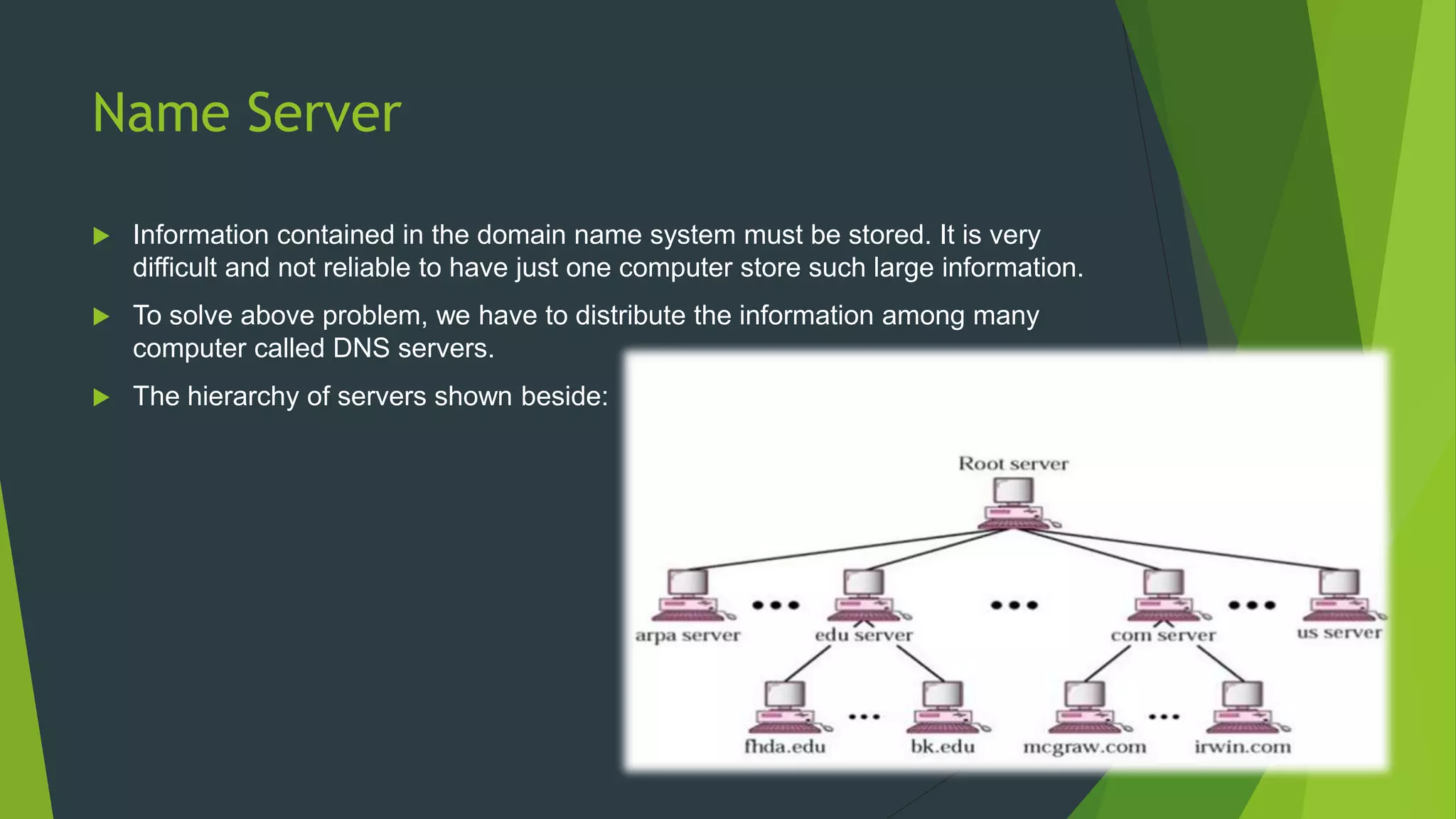
- DNS information is stored across multiple name servers to prevent a single point of failure.
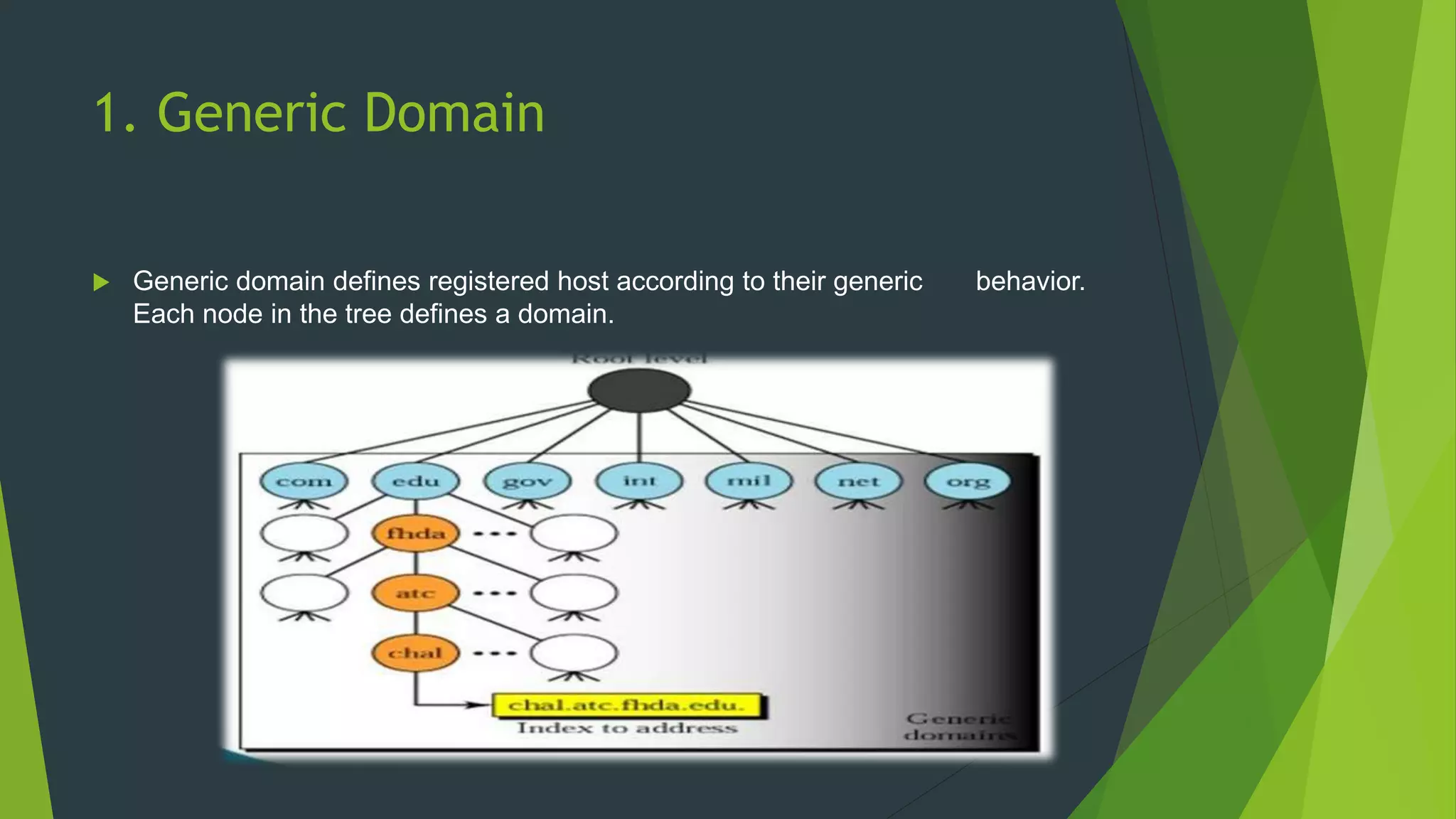
- The domain name space is divided into generic, country code, and inverse domains to organize names by usage and map addresses to names.
- Domain names are read from right to left with the top-level domain at the far right, working left through more specific subdomains.