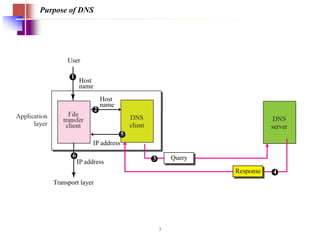
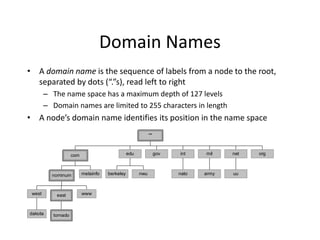
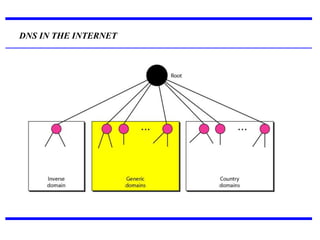
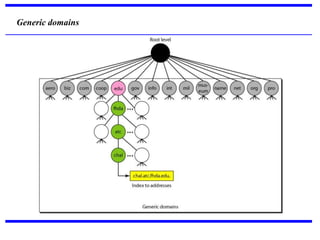
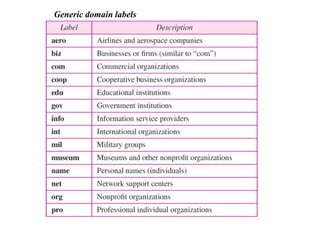
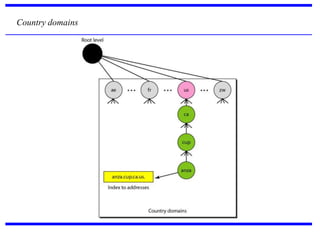
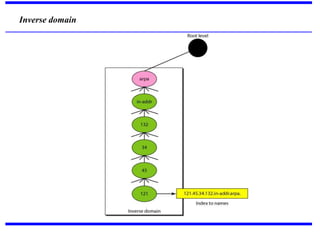
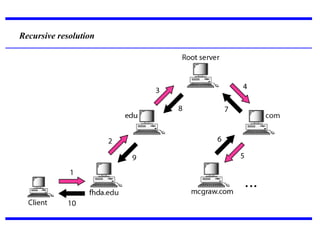
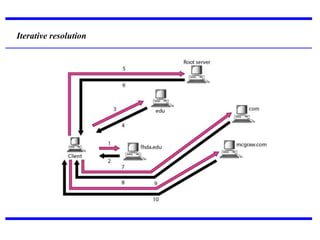
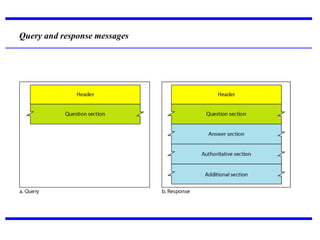
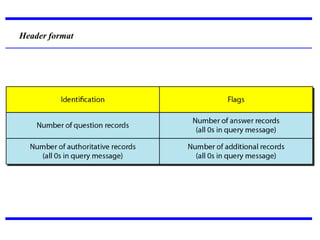
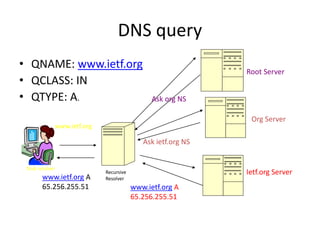
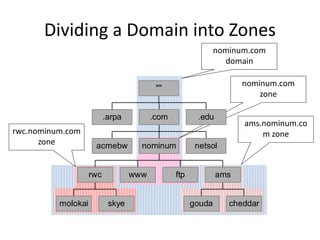
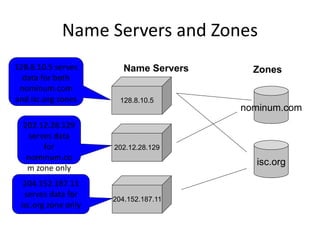
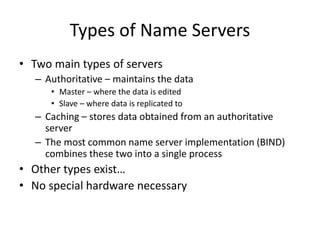
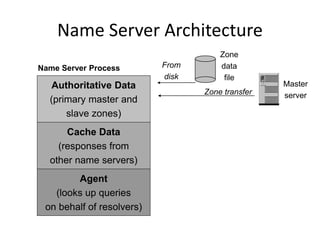
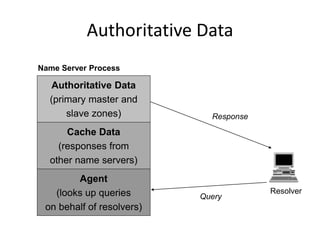
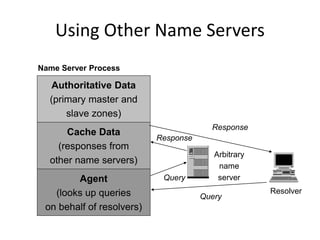
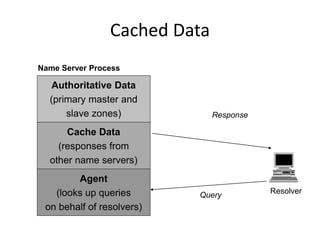
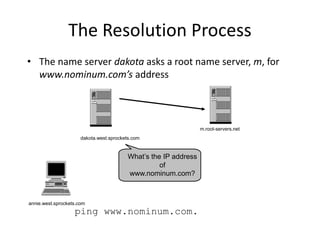
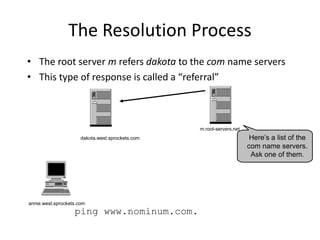
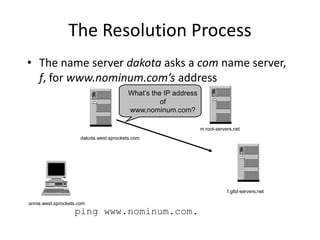
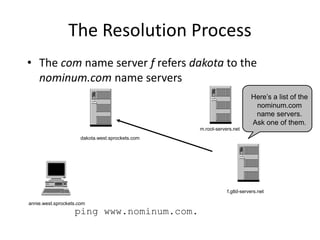
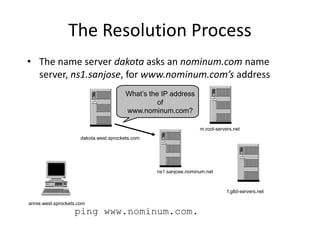
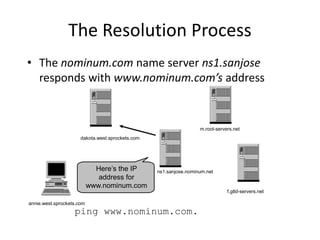
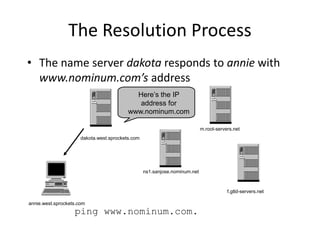
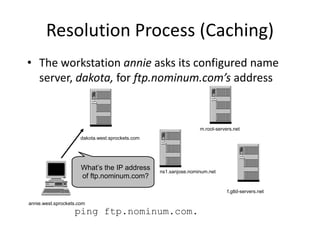
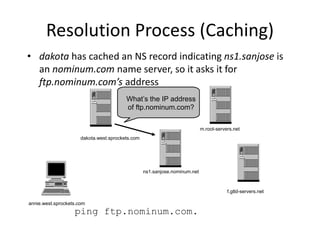
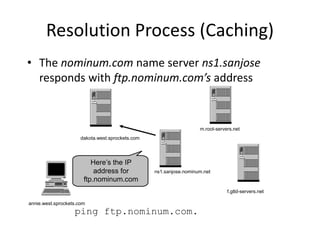
DNS is a core internet protocol that maps domain names to IP addresses. It allows users to connect to internet resources using easy to remember names instead of hard to remember IP addresses. DNS works by having a distributed database of domain name resources across various name servers that are organized hierarchically. A DNS query starts at the root servers and recursively moves down the hierarchy until it reaches an authoritative name server that can provide the IP address associated with the requested domain name. Caching is used to improve performance so that DNS servers can quickly respond to subsequent queries without having to recursively traverse the hierarchy again.