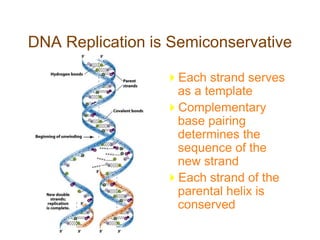
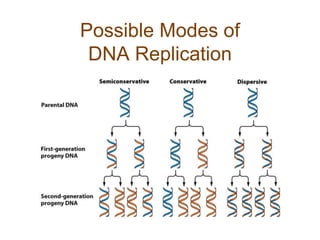
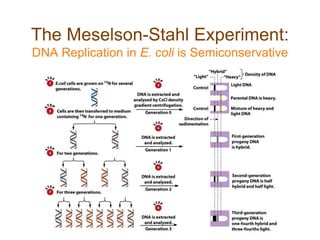
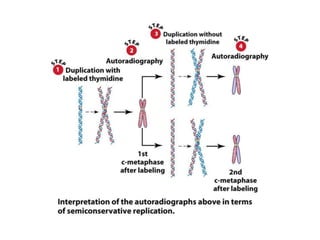
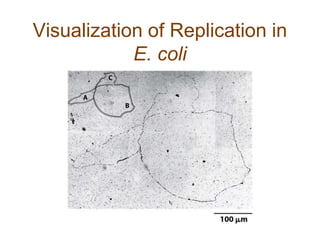
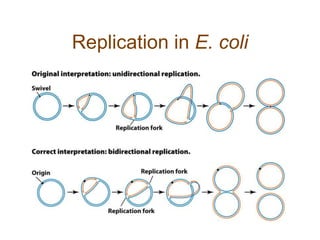
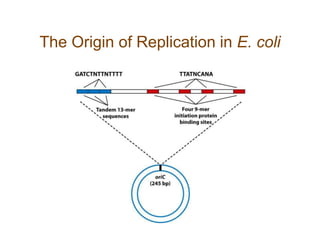
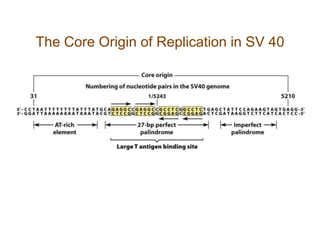
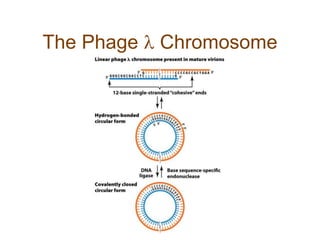
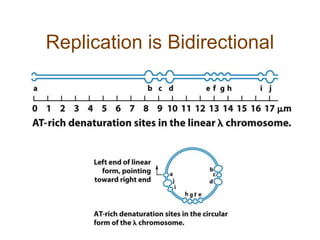
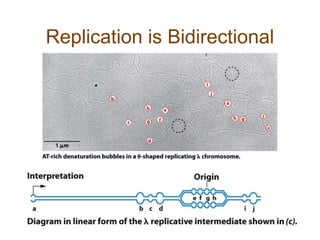
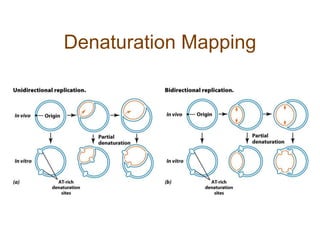
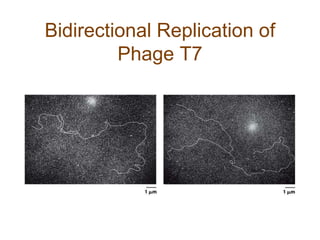
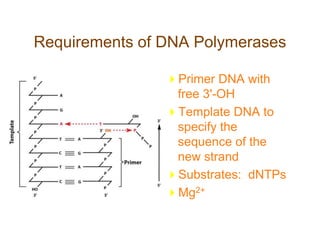
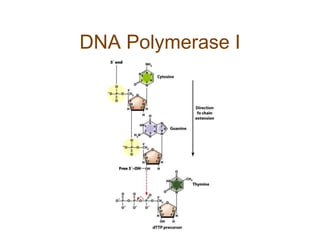
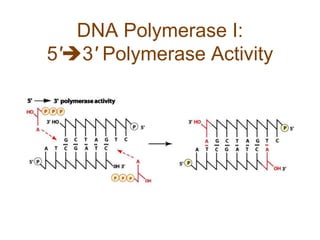
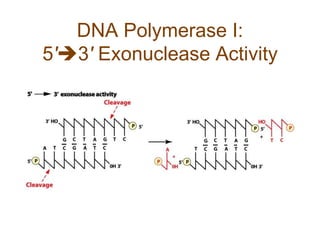
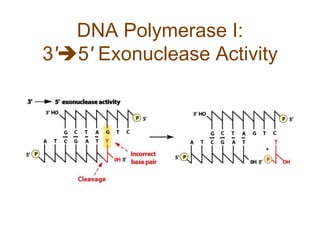
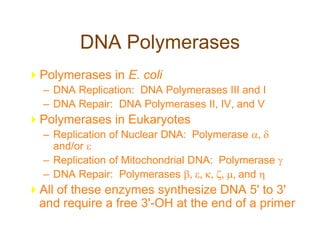
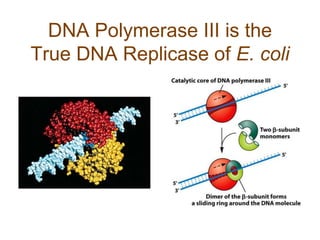
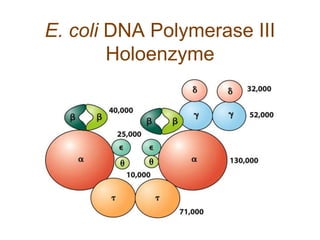
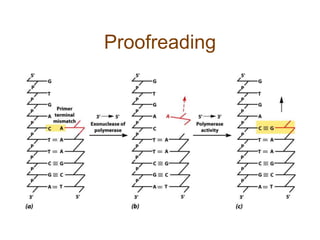
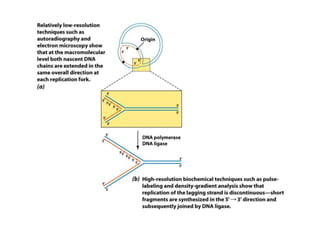
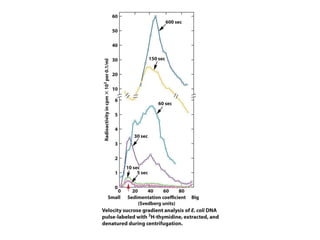
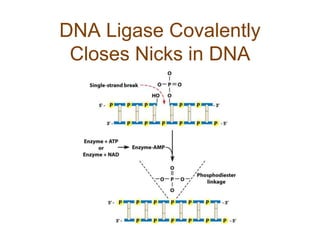
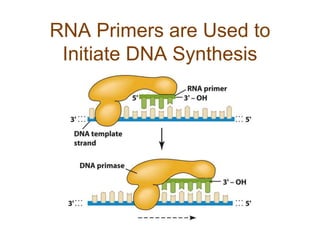
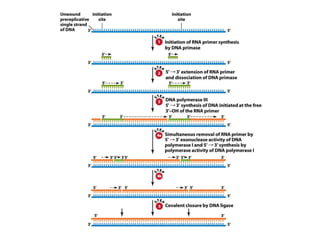
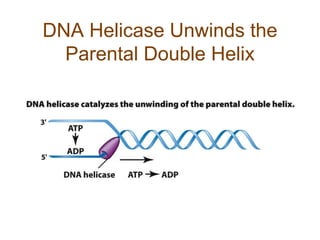
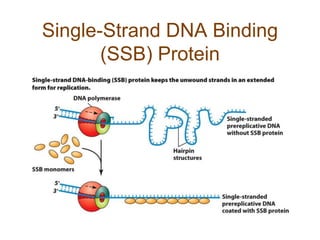
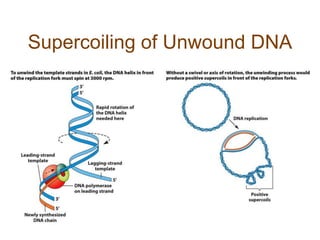
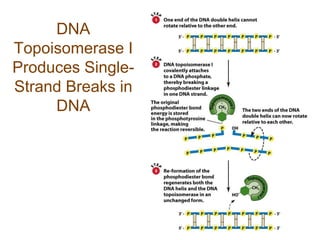
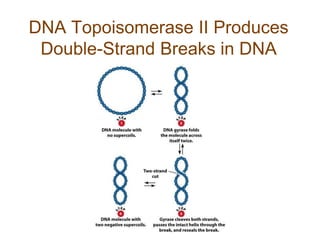
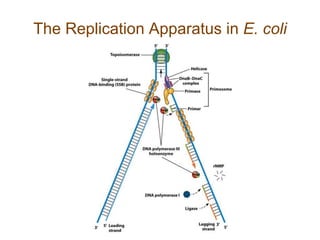
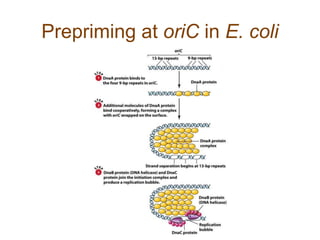
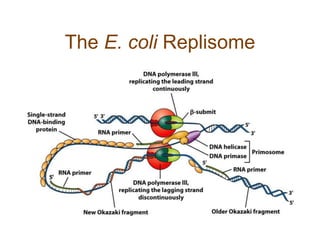
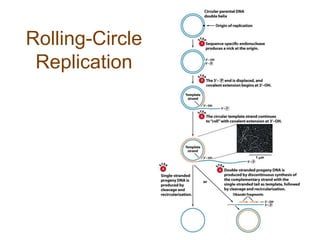
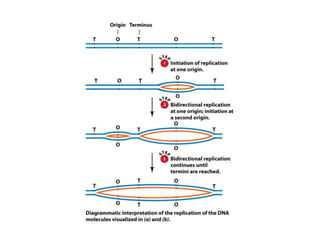
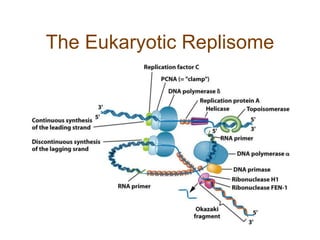
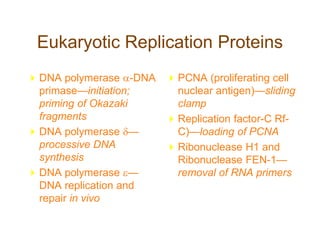
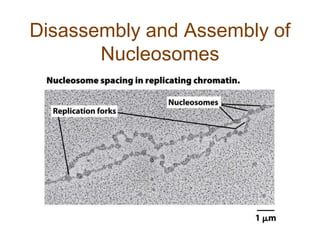
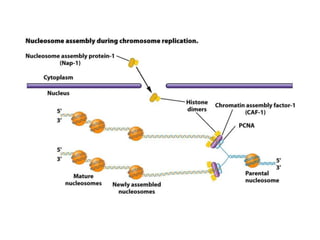
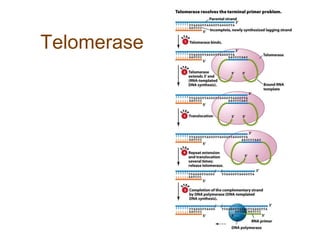
DNA replication occurs through a semiconservative mechanism whereby each parental DNA strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This process requires the coordinated action of multiple DNA polymerases and other proteins assembled into a replisome. In eukaryotes, DNA replication initiates from multiple origins and must overcome challenges like replicating through nucleosomes and maintaining telomere lengths.