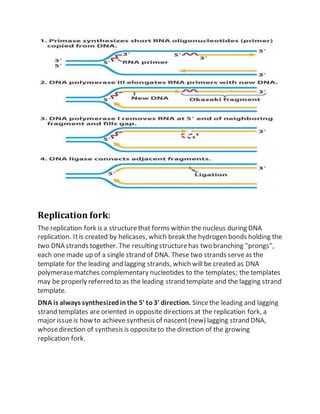
DNA replication is the process by which DNA duplicates itself for transmission to new cells. It occurs during S phase of the cell cycle and involves unwinding the DNA double helix, exposing the bases. Enzymes then link complementary nucleotides to form new strands. There are three proposed models for how replication occurs - semi-conservative, conservative, and dispersive. Replication requires a set of proteins and enzymes and energy in the form of ATP. It has two basic steps - initiation and elongation - and two basic components - a template and primer.