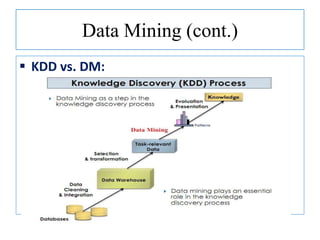
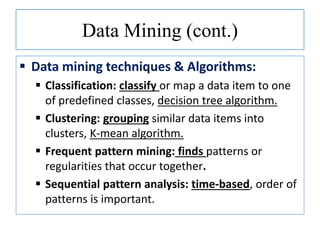
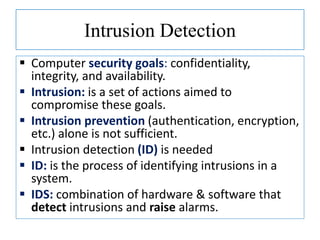
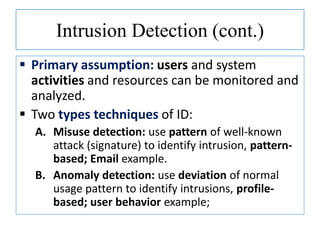
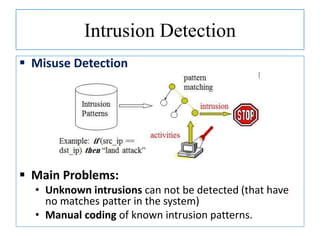
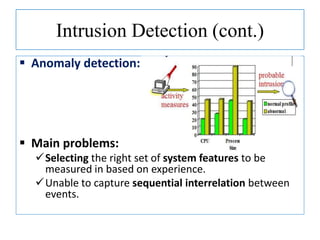
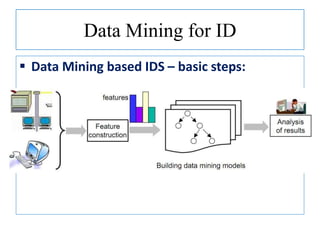
The document discusses using data mining techniques for intrusion detection. It first defines key concepts like data mining, knowledge discovery in databases, and intrusion detection. It explains that data mining can be used to build predictive models for misuse detection using classification algorithms trained on labeled audit data. For anomaly detection, data mining identifies abnormal behaviors that deviate from profiles of normal user activities. The document provides an overview of how data mining approaches can help address limitations of traditional misuse and anomaly detection methods for intrusion detection systems.