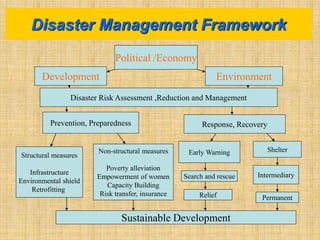
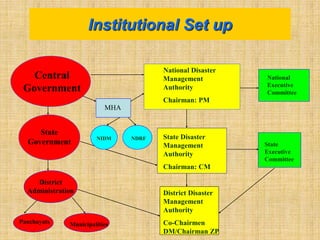
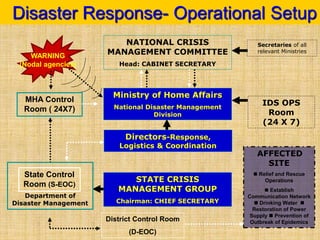
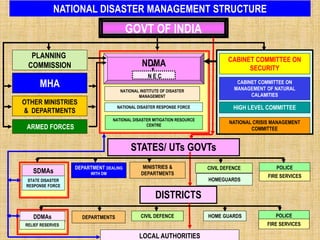
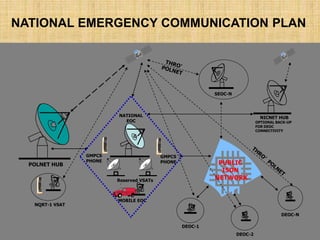
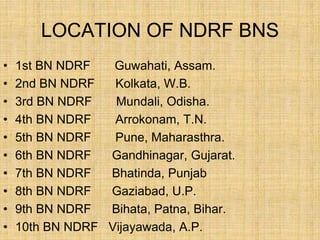
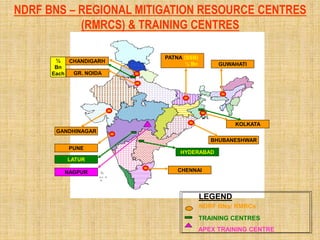
The document provides an overview of disaster management concepts and frameworks in India. It discusses how disasters are inevitable and proactive mitigation efforts are crucial. Major disasters between 1993-2005 exposed weaknesses in India's disaster response system and highlighted the need for policy reforms. This led to the enactment of the Disaster Management Act of 2005, which established authorities and institutional frameworks at the national, state, and district levels. It also summarizes key initiatives by the Indian government to strengthen disaster response, including setting up the National Disaster Response Force and emergency operation centers.





































![• NCRMP to cover 13 cyclone prone States/Union Territories
[cost US $ 365 million/ Rs 1650 cr.]
• Main elements of the project:
– Strengthening of cyclone tracking and monitoring
– Developing cyclone shelters in coastal areas
– Regenerating mangrove forests as protective shields for
coastal settlements
– Supporting State/UTs for taking up high priority cyclone
risk mitigation activities
– Providing technical assistance for hazard risk
management capacity building
National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dmbasicconcepts-221113025112-452bd18f/85/DM-Basic-Concepts-ppt-45-320.jpg)


