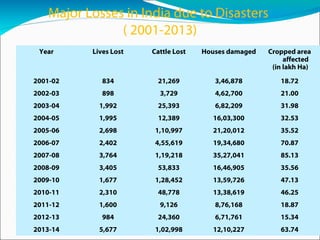
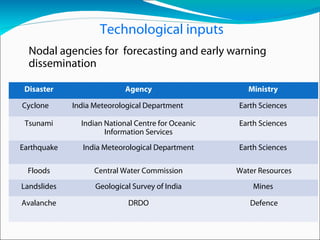
This document provides information about disasters in India. It discusses definitions of disasters according to the DM Act 2005 and data on different types of disasters from 1900-2009. It also outlines vulnerability in India, major losses from 2001-2013, the Disaster Management Act of 2005 including institutional mechanisms and financial arrangements. It discusses policies, plans, guidelines and technologies for forecasting and early warning. Key aspects around mitigation, preparedness, response and challenges are summarized.