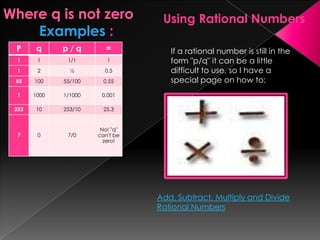
The document discusses the concept of division and rational numbers, explaining how division involves finding quotients of integers and how it leads to the introduction of rational numbers, which can be represented as fractions. It provides examples of division and describes the relationship between division and multiplication through examples and definitions. Additionally, it touches on the historical context regarding rational and irrational numbers, referencing Pythagoras and Hippasus.