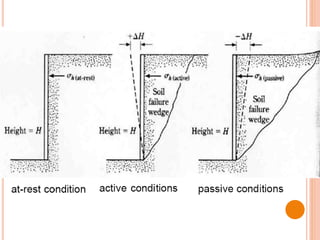
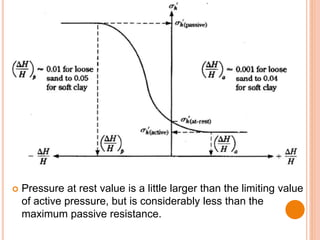
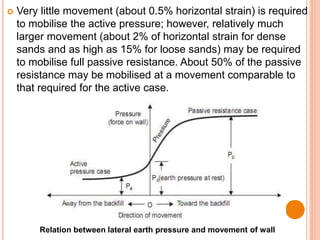
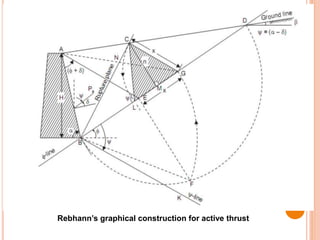
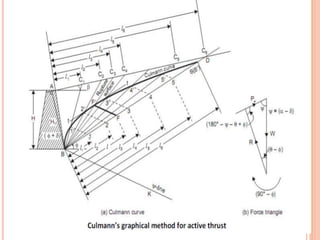
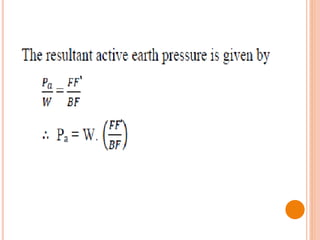This document discusses lateral earth pressure and provides details on Rankine's theory and graphical methods for determining active and passive earth pressures. It explains that lateral earth pressure is exerted by soil on retaining structures and depends on whether the structure is stationary or moving towards/away from the soil mass. Rankine's theory assumes dry, homogeneous soil and a vertical wall. Rebhann and Culmann's graphical methods can be used to locate the failure plane and determine the magnitude and direction of lateral earth pressures based on the soil's friction angle and the structure's orientation.