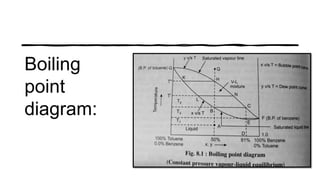
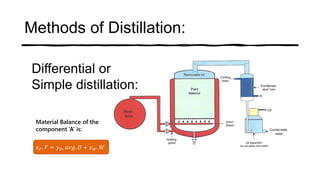
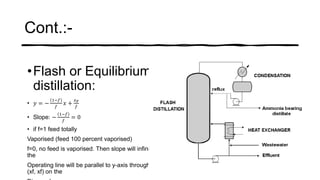
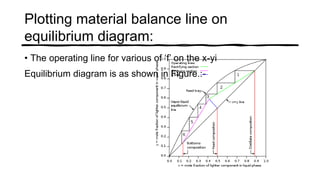
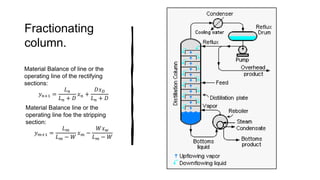
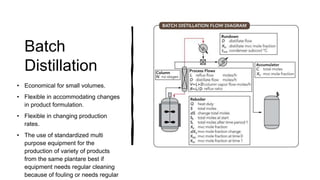
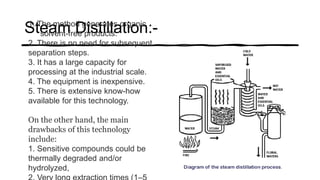
Distillation is a process that separates liquids in a mixture based on differences in their boiling points. It works by heating the mixture to vaporize components, then cooling to condense them. There are several types including simple, flash, and rectification distillation. Rectification uses a fractionating column with trays to continuously refine the vapor into pure products. Key factors that determine separation include relative volatility and vapor-liquid equilibrium curves. Distillation is widely used in oil refining and other industrial separations.