DNA profiling and its legal applications were discussed. Key points include:
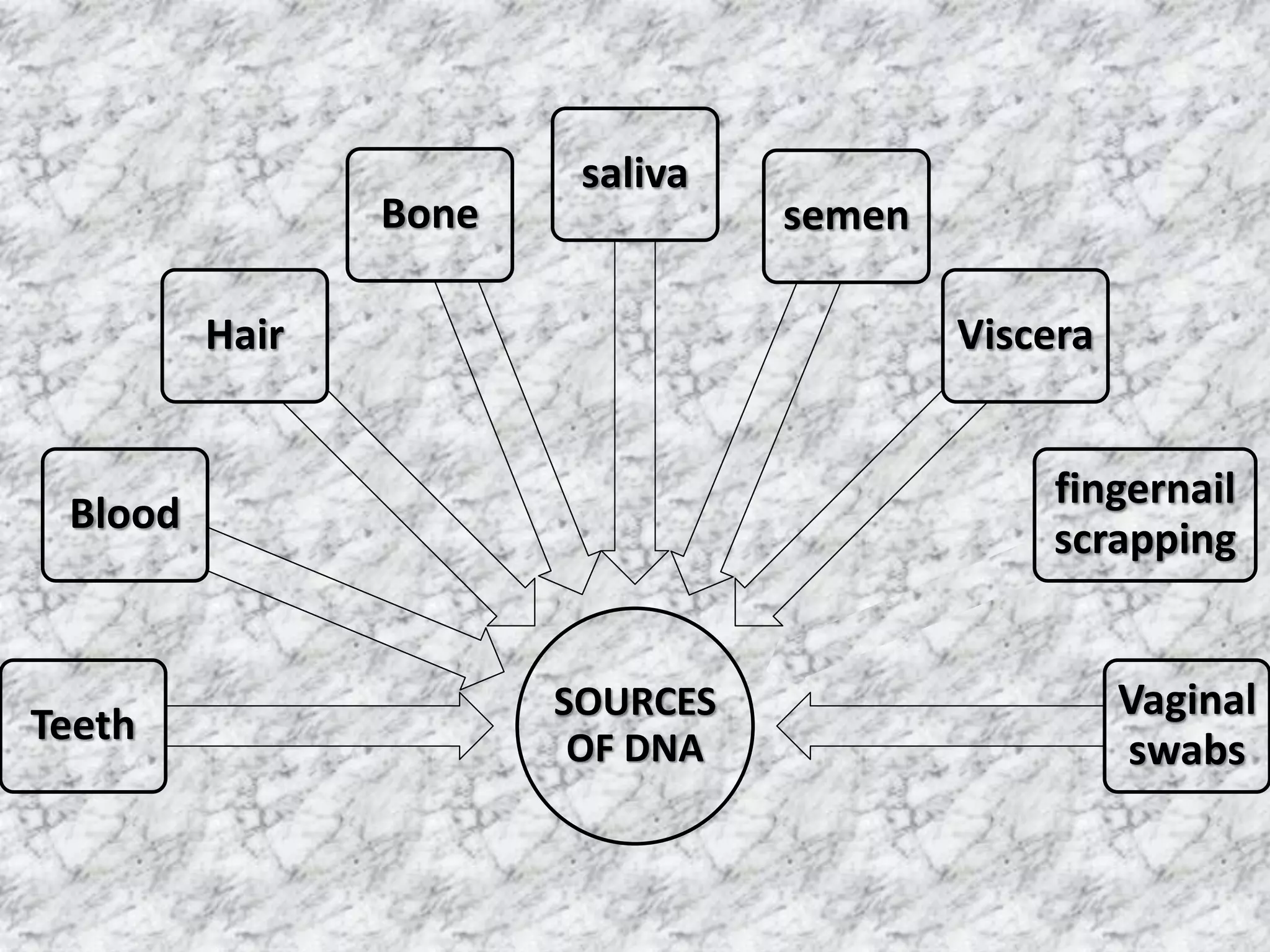
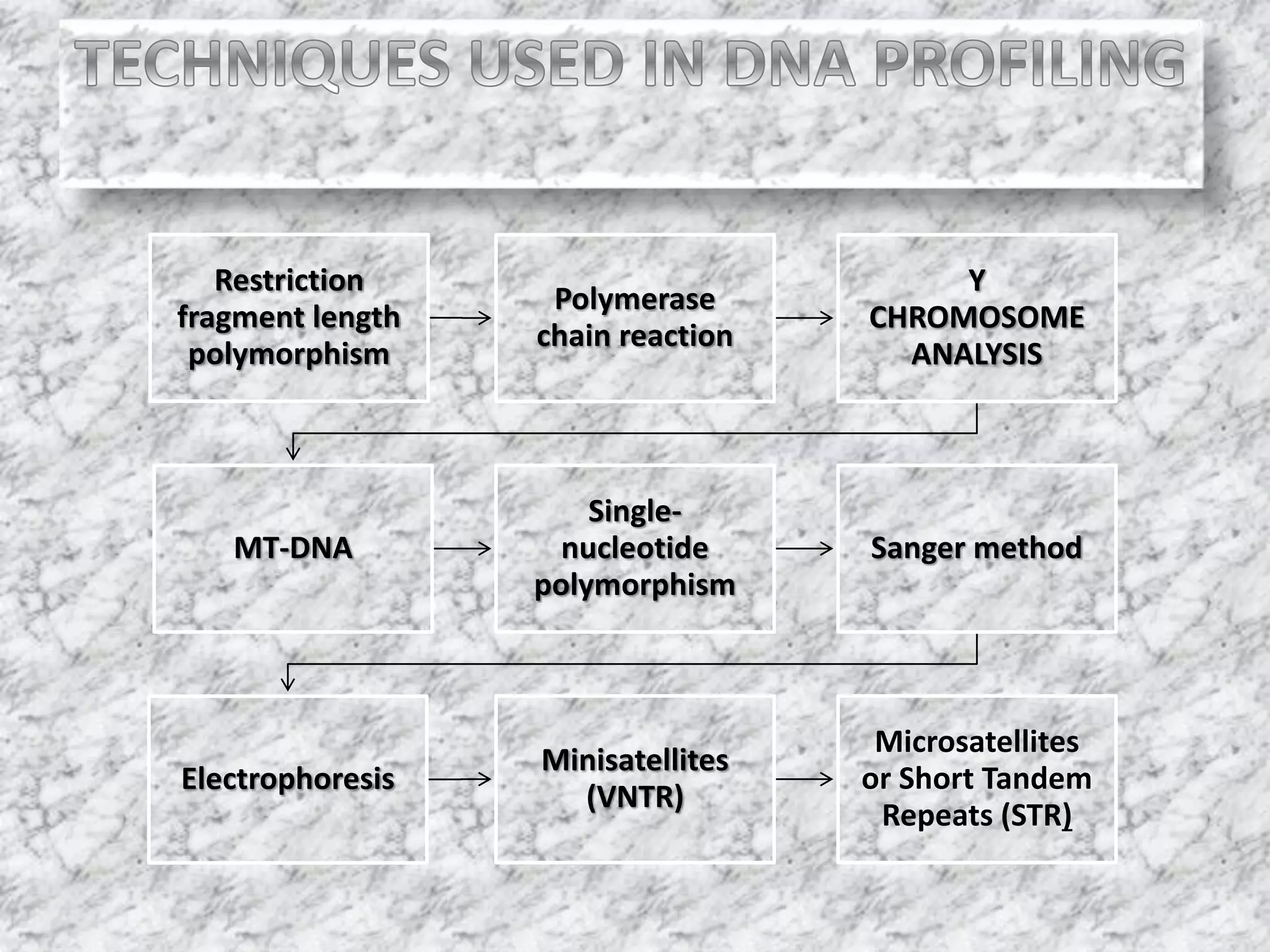
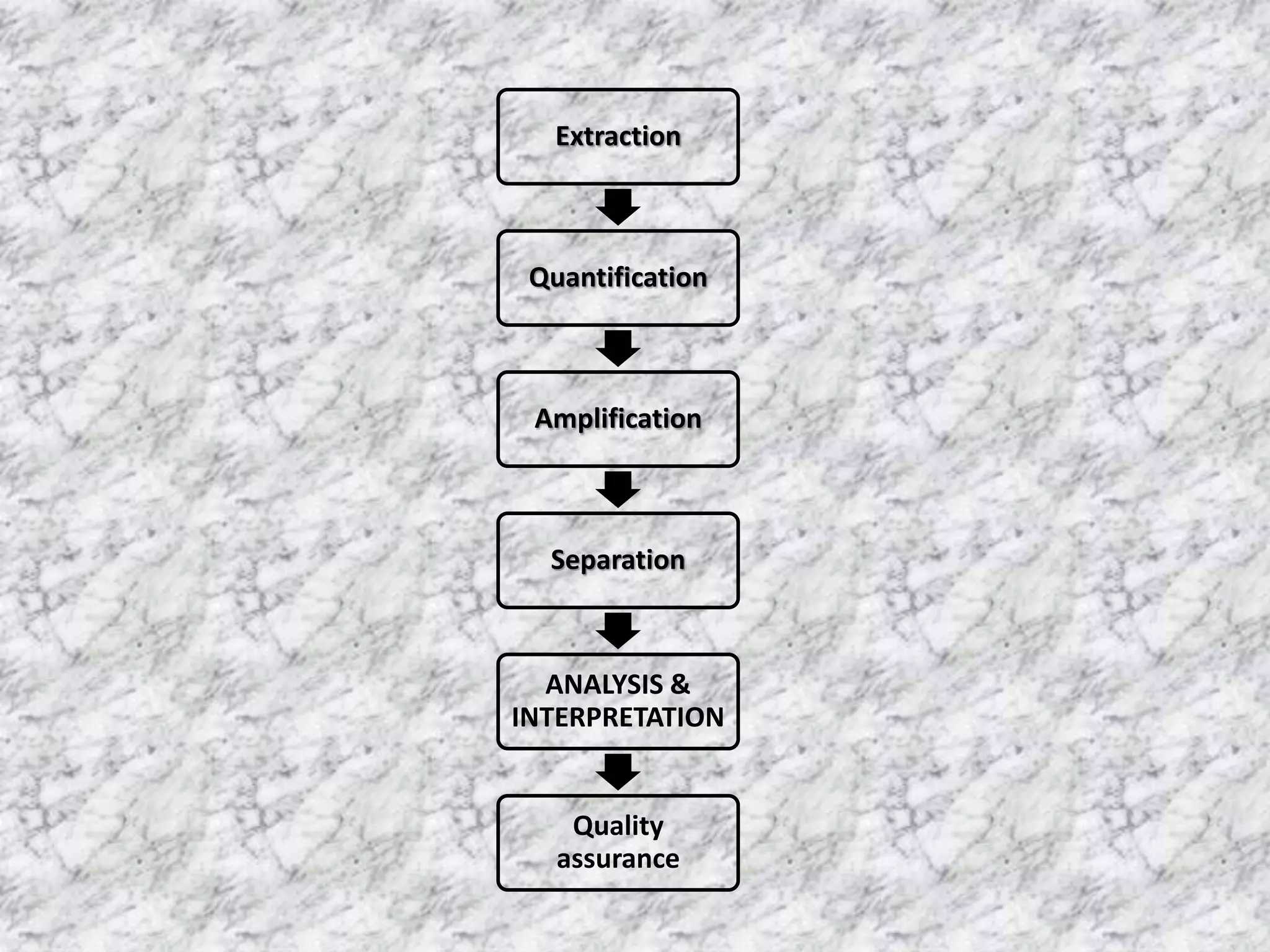
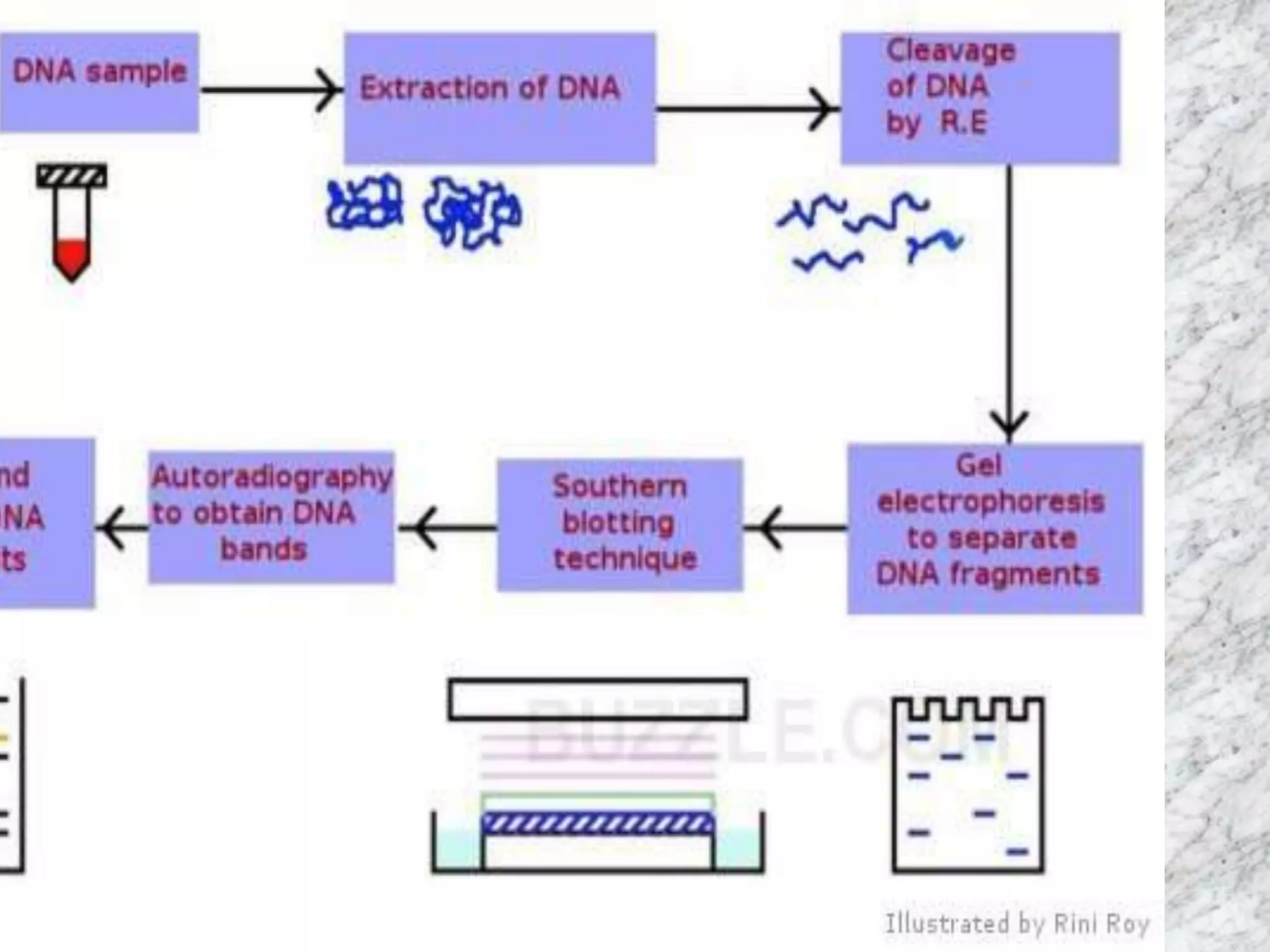
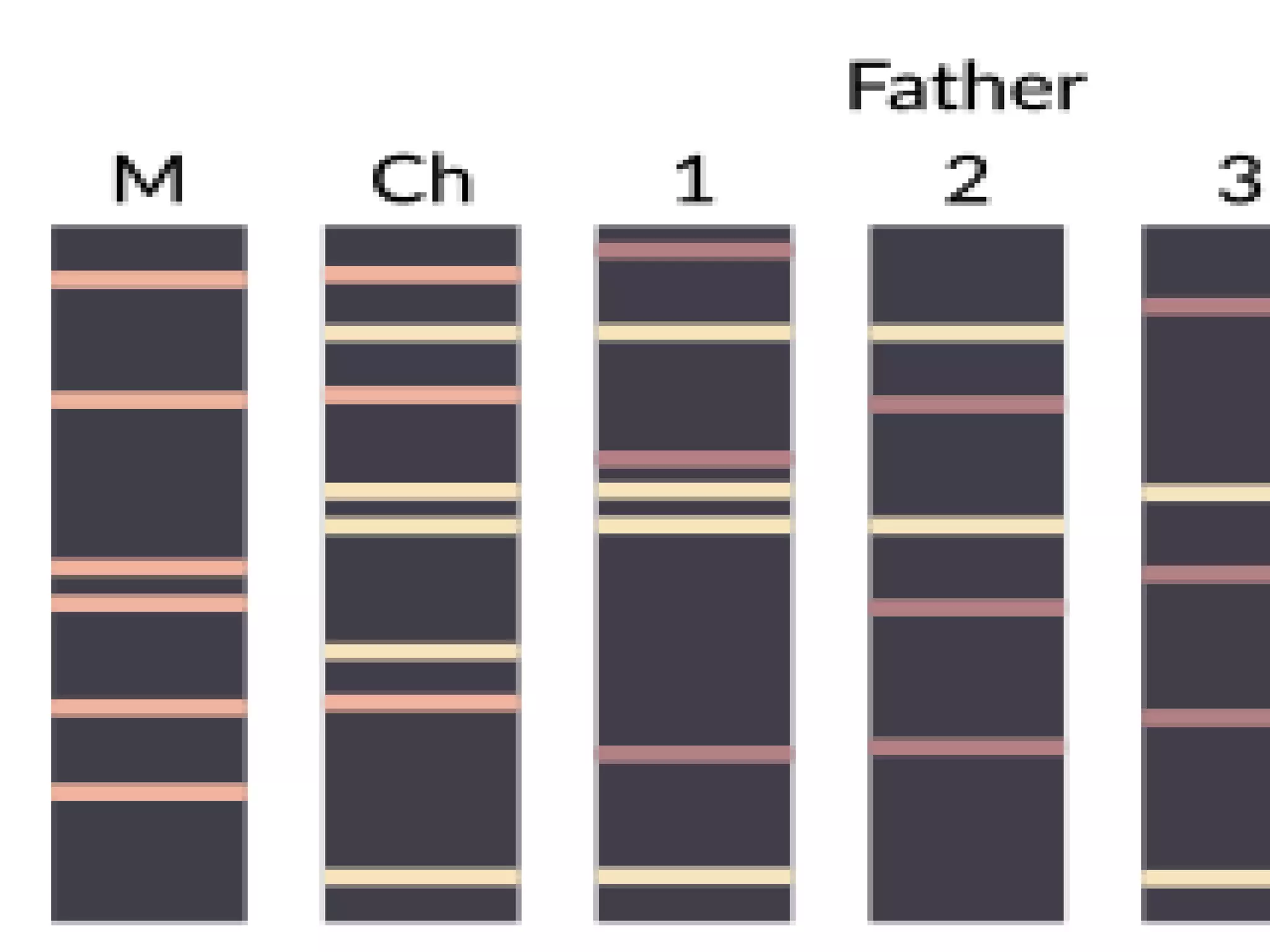
1) DNA profiling involves analyzing variable repetitive sequences in non-coding regions to obtain a unique genetic profile for identification.
2) The first use of DNA fingerprinting in a criminal case in 1986 helped exonerate a falsely accused man.
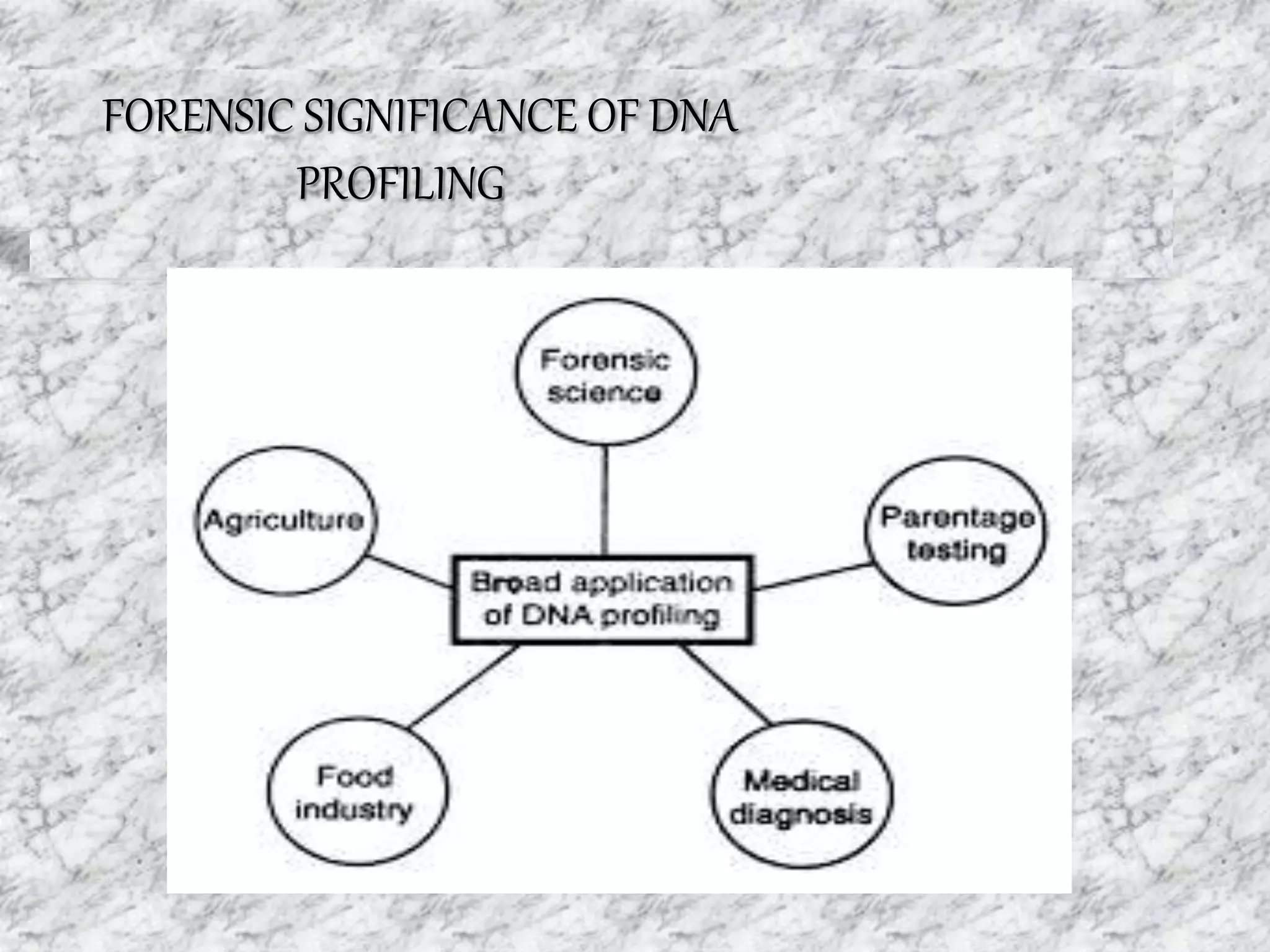
3) DNA has significant forensic applications such as identifying suspects in murder, sexual assault, and disputed parentage cases.
4) DNA analysis also has legal implications including the right to privacy versus right to information in criminal investigations.