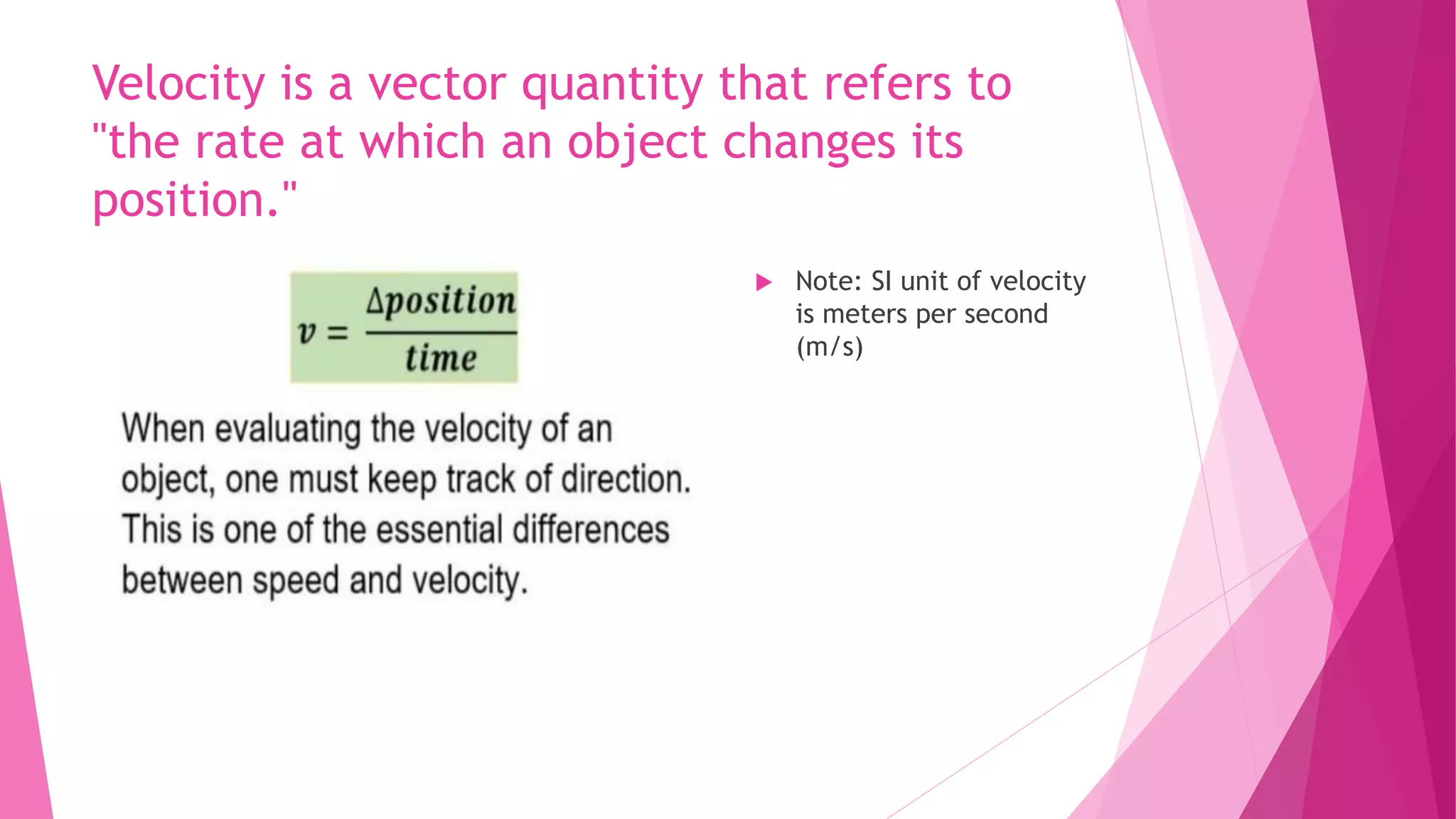
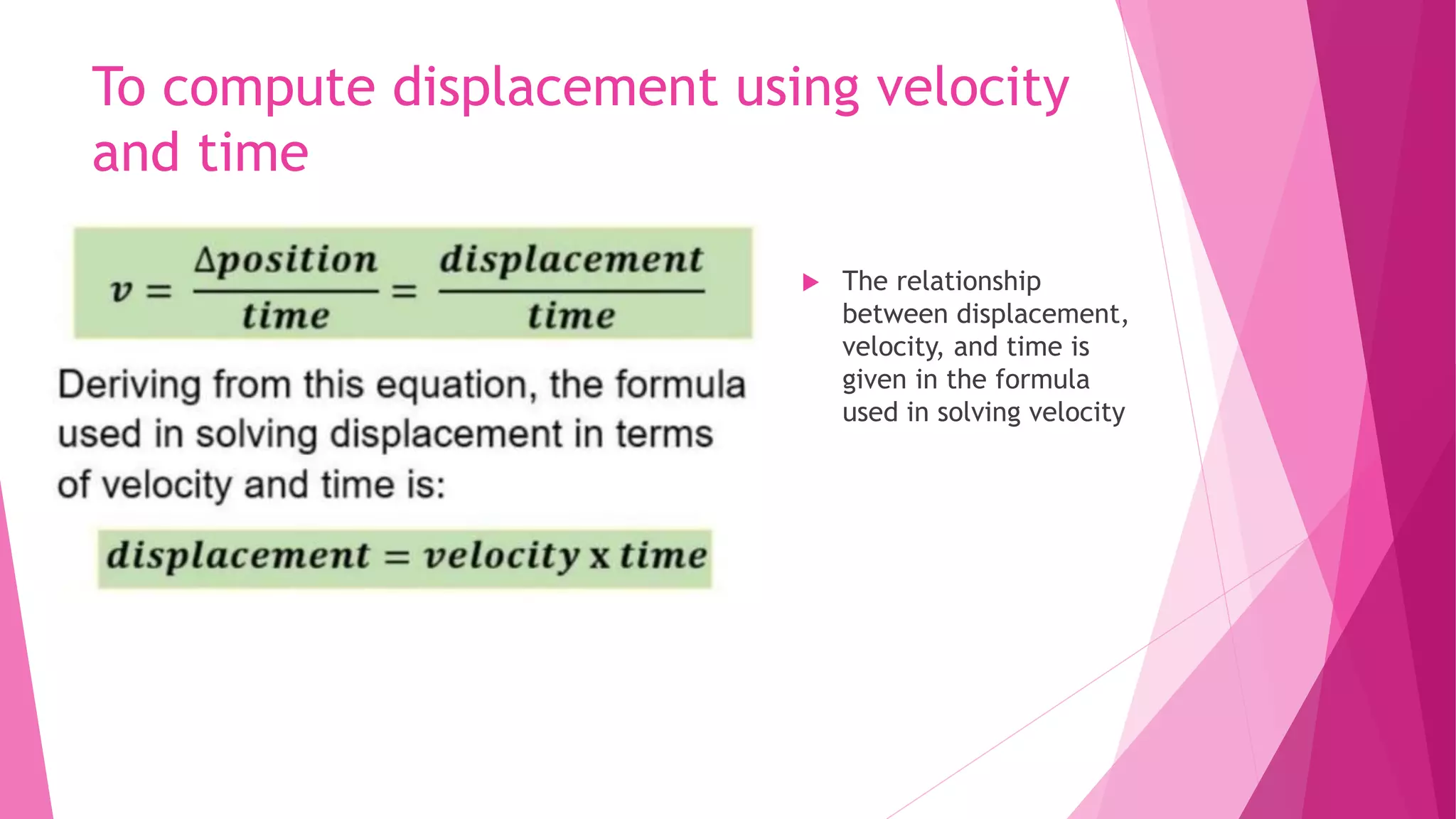
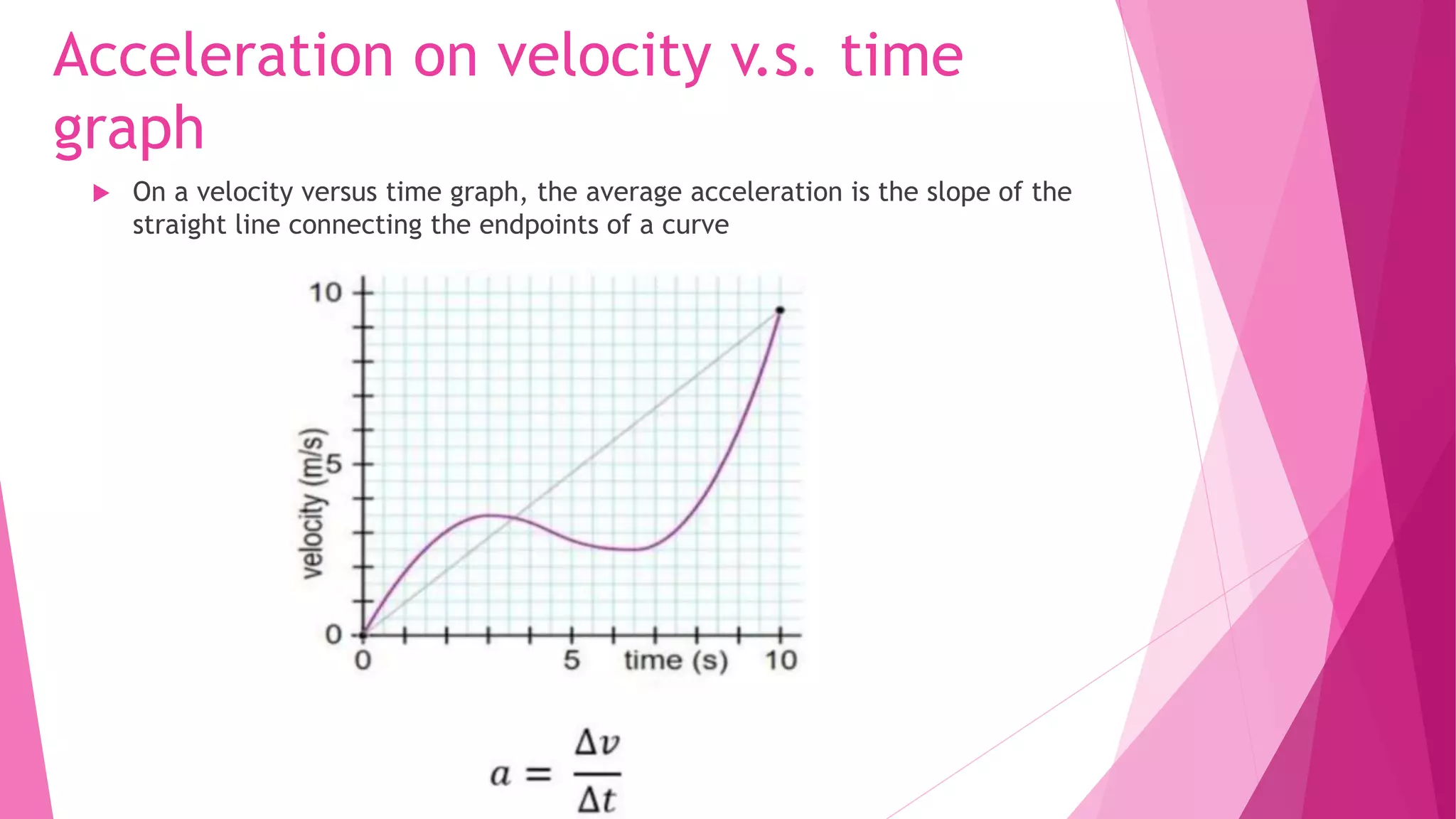
This document discusses key concepts in kinematics including displacement, velocity, acceleration, and how they relate to each other and can be represented graphically. It defines displacement as a change in position, velocity as the rate of change of position, and explains how to calculate displacement using velocity and time. It also describes different types of graphs used in kinematics such as velocity vs. time graphs, acceleration vs. time graphs, and position vs. time graphs and how to interpret features of these graphs like slope, area under curves, and curvature to determine properties of an object's motion like velocity and acceleration.