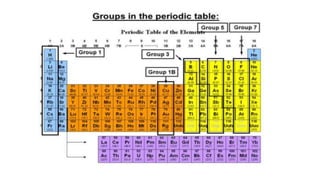
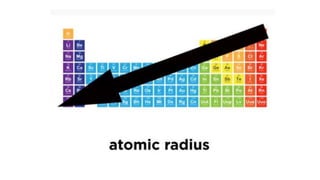
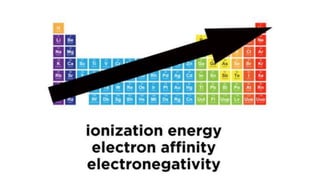
The periodic table arranges elements by atomic number and recurring properties. It contains 18 groups and 7 periods. Groups 1-2 and 13-18 are representative elements including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and noble gases. Groups 3-12 are transition metals. The document discusses common properties of several groups including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, and halogens. It also covers valence electrons, atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity trends in the periodic table.