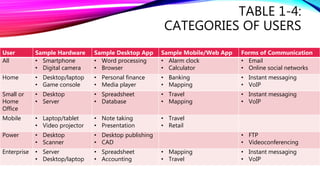
This document provides an overview of digital literacy and introduces various types of computers and devices. It discusses that digital literacy involves having current knowledge of technology like computers, mobile devices, the internet. It then defines what a computer is and describes components like hardware, software, and personal computers. It also discusses different types of personal computers like laptops, tablets, desktops and their features. The document further introduces other devices like servers, smartphones, digital cameras, portable media players, e-book readers and game consoles. It also covers input and output devices used with computers.