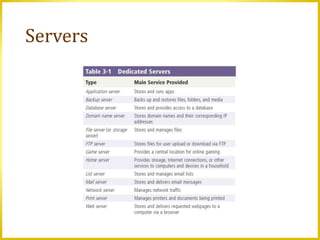
This document discusses various computer and mobile devices, including their characteristics and uses. It covers desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, digital cameras, portable media players, servers, terminals, cloud computing, game devices, embedded computers, ports and connections. The document also addresses protecting hardware from theft or damage and health concerns related to technology use.